This section shows how to run a pipeline or restart a failed pipeline run. It also has examples showing different pipeline run scenarios.
| You can also use Perl API commands through ec-perl and ectool, REST API commands, and DSL scripts to model and run pipelines. For more information, refer to Introduction. |
Starting from the Pipelines list:
-
Select Run on the pipeline you want to start. Optionally, you can choose a previously run pipeline.
-
If the pipeline has required parameters to run the pipeline, enter the parameter values. If you are rerunning a pipeline, it will use its parameter values from the previous run or use new values you provide.
-
View the real-time progress of the pipeline run.
-
Progress is shown in percentage complete.
-
Tasks requiring a response are denoted by the following:
-
 — Manual attention needed, and you are on the approver’s list.
— Manual attention needed, and you are on the approver’s list. -
 — Manual attention needed, and you are not on the approver’s list.
— Manual attention needed, and you are not on the approver’s list.The following example shows that the entry gate of the DEV stage has gate approvals that require approval before the pipeline can enter the QA stage.
 Figure 1. DEV stage entry gate
Figure 1. DEV stage entry gateSelect Response Required to view the gate approvals and the required reviewers.
Select the hand icon under the Manual column to access the list of required reviewers, in this case, for the DEV stage entry gate.
-
-
-
Click in a stage to view the details of the pipeline stage summary.
For examples of pipeline stage summaries, refer to Pipeline stage summary.
-
Select View previous Pipeline Runs to access previous runs of this pipeline.
Pre-running a task
For tasks configured to run out of order, you can pre-run a task. Only the specified task runs; execution does not continue to the following tasks and stages. When pipeline run execution reaches a task which has already run, the pre-run task is skipped. If the pre-run task is still running, the pipeline execution waits for it to complete and then continues on to the following tasks. A task can be pre-run if:
-
It is configured to run out of order. Refer to Configuring Pre-Run Tasks for more information.
-
All pre-conditions, on both the task itself and a stage/gate containing the task, must evaluate to true.
-
No pending runtime wait dependencies on the task itself or stage/gate containing the task.
-
If configured with wait for start date, the planned start date requirement for stage/gate and task is met.
Error handling on the specified task has no impact on its pre-run execution: the task runs and stops regardless of success or failure. However, when the regular execution reaches a pre-run task that has failed and has error handling defined as:
-
Stop on error: Pipeline execution stops.
-
Continue on error: Pipeline execution continues to the next task.
-
Retry: The task is retried.
To pre-run a task, locate it in the pipeline run, then select Pre-Run Task from the task’s Actions menu.
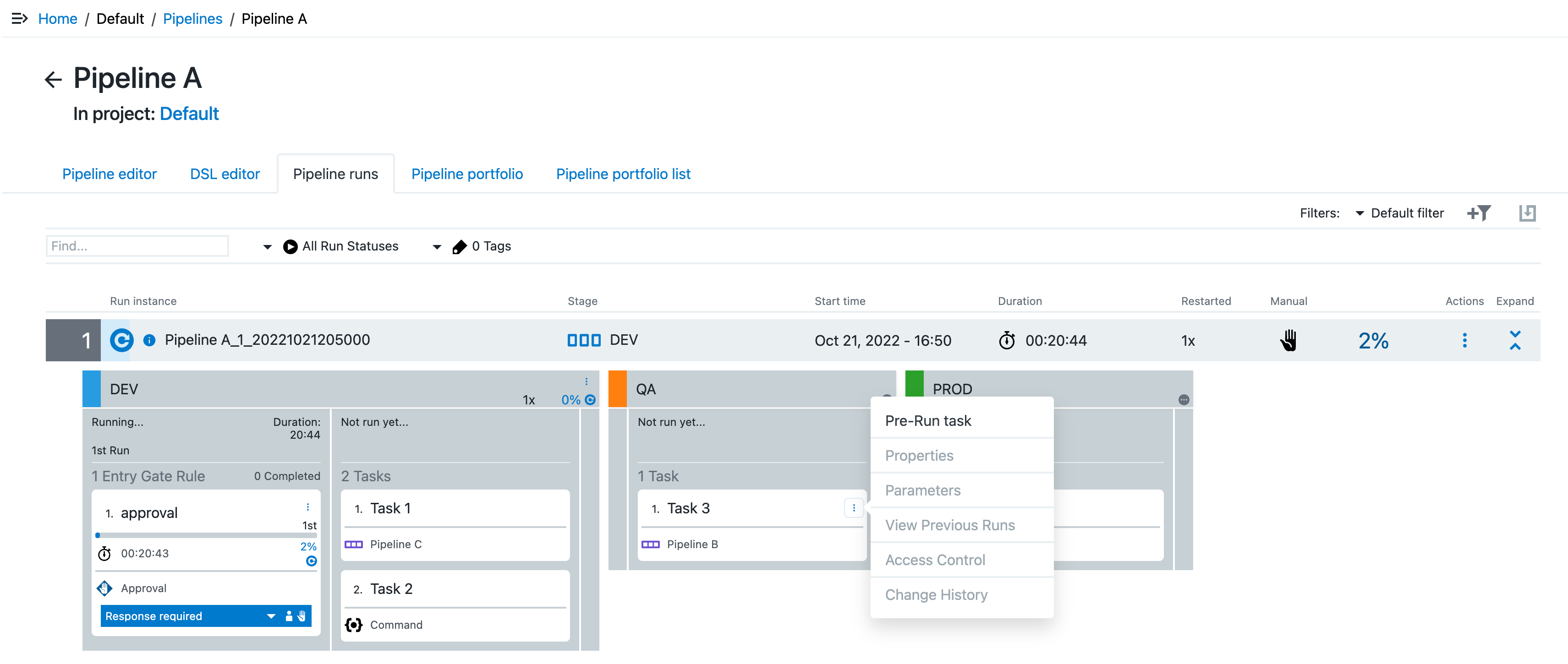
A completed pre-run task is denoted with a dot and its containing stage is denoted with a multi-colored header.
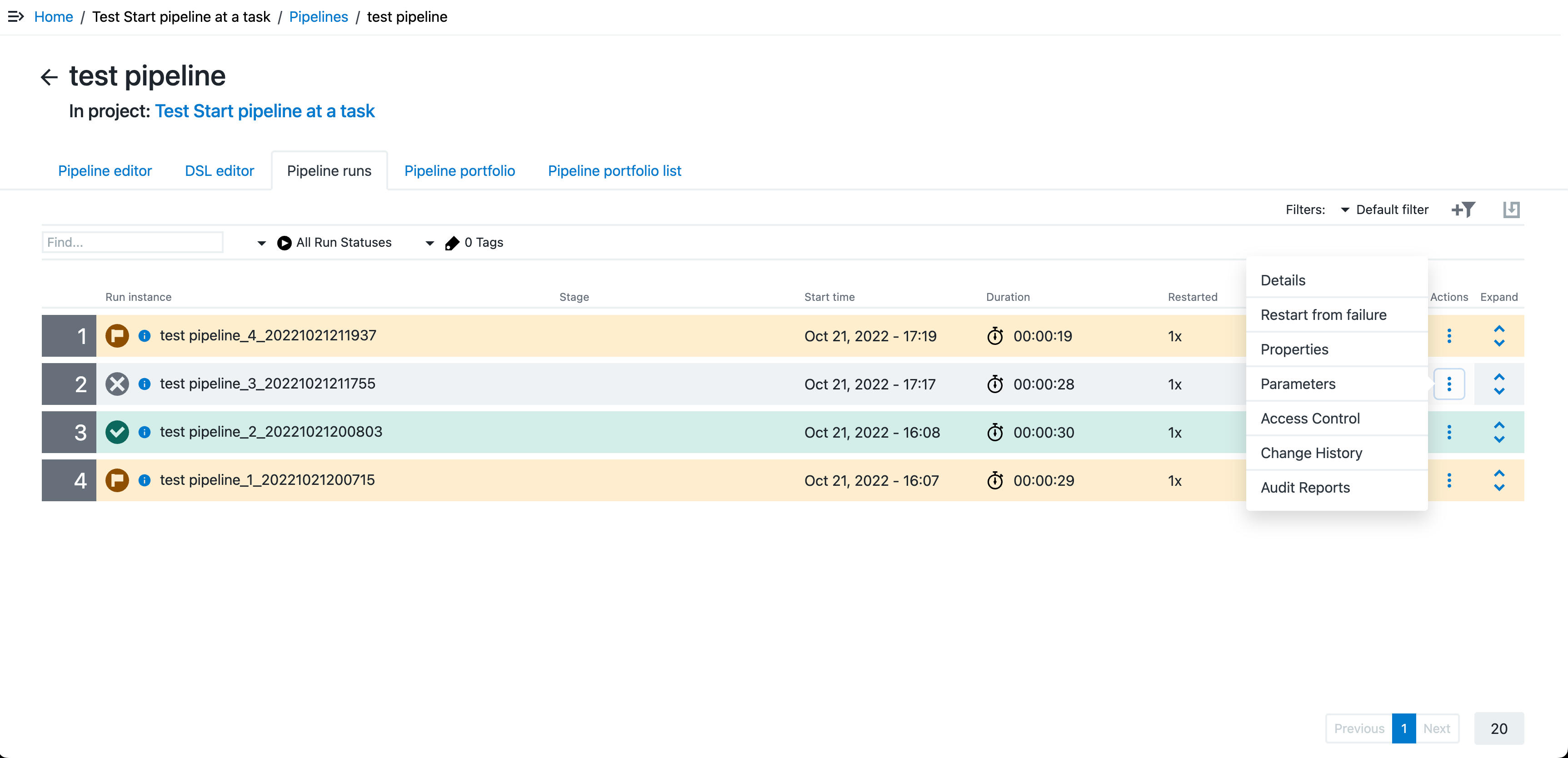
Restarting a Failed Pipeline Run
A restart capability for failed pipeline runs lets you configure a pipeline run to restart from the last failed task after you update the task definition and fix the issues that caused the failure. The user restarting the pipeline must have execute privileges on all tasks, rules, and stages after the task that is being restarted, including the failed task itself.
A pipeline run is restartable
-
If the last executed task in the run has a failure outcome, provided its error handling is not configured as Continue on Error. Any prior failed tasks—in the same or previous stages or gates—with Continue on Error error handling enabled are ignored.
-
If the last stage has no tasks in it, and it is in error because of a run condition/precondition evaluation error.
To restart a failed pipeline, select Restart from failure from the pipeline run’s Actions menu. Restarting a pipeline prompts you enter a comment about the restart.
Pausing or resuming a pipeline run
On the Pipeline list or Pipeline runs screens, select the three-dots menu and either Pause run or Resume run to interrupt or restart a pipeline run. When pausing a run, tasks will be handled as follows:
-
All running tasks will continue until completion.
-
A manual or wait for the precondition task will pause immediately. However, you can still approve or provide conditions while the pipeline is paused. When approval or conditions are provided, these tasks will run to completion and the pipeline will remain paused.
-
A manual retry on error task will pause immediately. You will have one of the following options:
-
If the task is paused before retry, you will be able to retry the task while the pipeline is paused.
-
If the task is paused after retry, you will have to
Resume runto receive the retry option.
-
-
An auto-retry task will pause immediately. You will have one of the following options:
-
If the task is paused before auto-retry attempt, then a retry will will occur.
-
If the task is paused after an auto-retry you will have to
Resume runto receive restart the auto-retry.
-
Viewing the Details of a Pipeline Run
You can view the details of a previous pipeline run from the Pipeline runs tab.
To view the details of a previous pipeline run:
-
Select Pipeline runs.
-
Select View previous Pipeline Runs to access the previous runs of this pipeline.
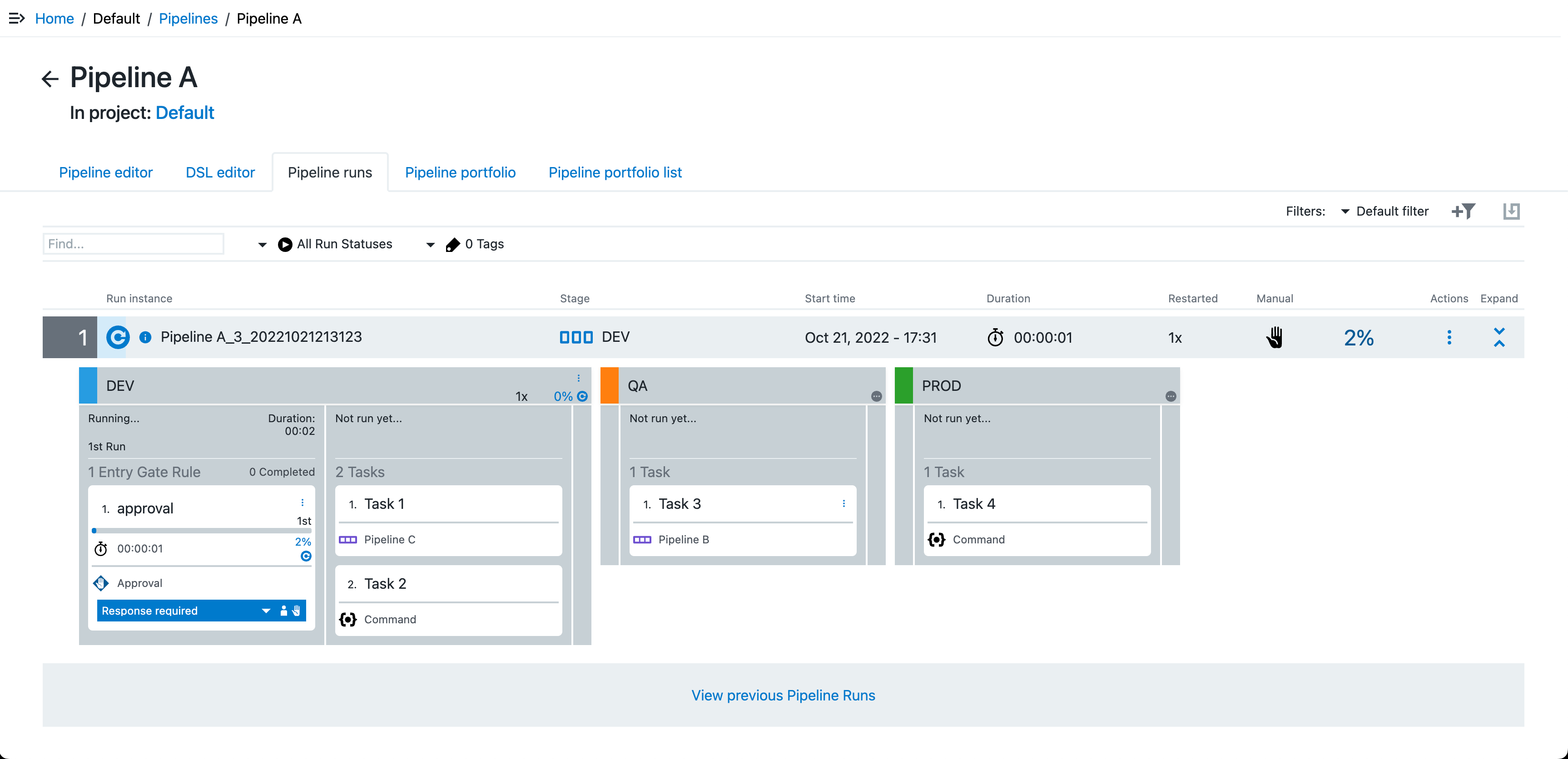 Figure 4. Select View previous Pipeline Runs
Figure 4. Select View previous Pipeline RunsThe previous pipeline runs display.
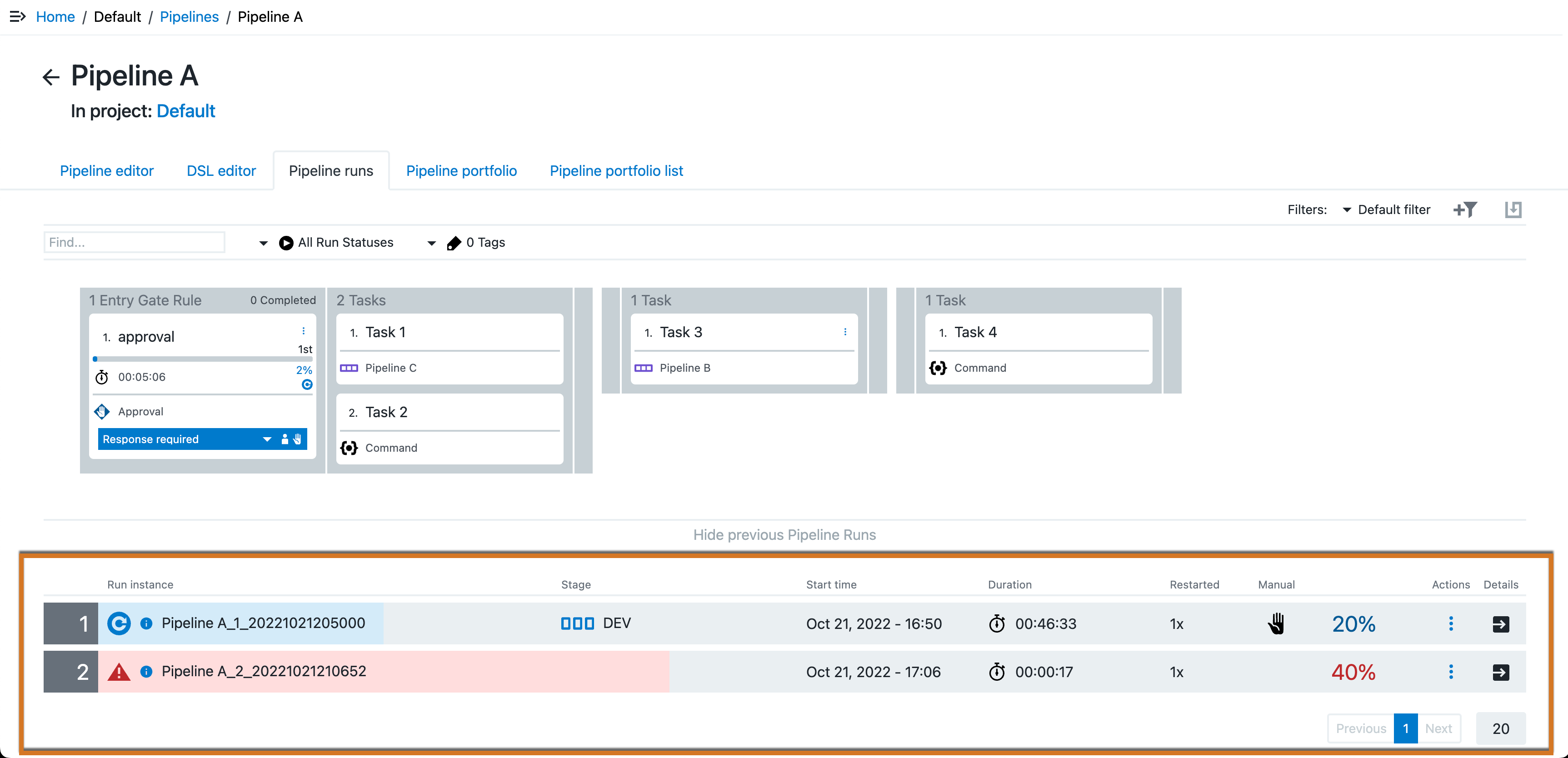 Figure 5. Previous pipeline runs displayed
Figure 5. Previous pipeline runs displayed -
(Optional) To access specific pipeline run details, select the Open Dialog arrow on the right of its row.