Single sign-on (SSO) allows a user to automatically gain access to multiple applications and services once their sign-in credentials have been authenticated. Authenticated users are able to bypass the sign-in screen when they want to take action in CloudBees Software Delivery Automation.
Kerberos SSO is a network authentication protocol that works on the basis of tickets that allow nodes, communicating over an unsecure network, to prove their identity to one another in a secure manner. Kerberos provides mutual authentication — both the user and the server verify each other’s identity. Kerberos protocol messages are protected against eavesdropping and replay attacks.
Kerberos builds on symmetric key cryptography, requires a trusted third party, and optionally may use public-key cryptography during certain phases of authentication.
Complete the following steps to configure Kerberos SSO at your site:
Kerberos SSO prerequisites
Before you configure Kerberos SSO, verify that:
-
Kerberos software is installed and configured on the server and client nodes.
-
Your system administrator has set up one or more Kerberos Key Distribution Centers (KDCs), and each KDC is accessible from every node in your environment.
-
Kerberos client software is installed on all hosts that are involved in Kerberos authentication.
This software is required to communicate with the KDC server but is not included in CloudBees Software Delivery Automation. A valid Kerberos configuration file that includes information about how to connect to the KDC, realm, and domain, such as a
krb5.conffile, must be provided for the client. Refer to the example Kerberos configuration file for more details.Note that Windows clients have Kerberos authentication built into the authentication process, so there is no need for additional software.
-
For each server in the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation ecosystem, the
ipaddress,hostname, andFQDNmust be resolvable.
Identifying the Kerberos SSO components
Identify the following components at your enterprise before proceeding. These components are used in the various stages of Kerberos SSO configuration.
| Component | Example value |
|---|---|
Active Directory domain |
|
Kerberos realm |
|
CloudBees Software Delivery Automation web server service |
|
CloudBees Software Delivery Automation web server service principal name |
|
CloudBees Software Delivery Automation web server service account |
|
CloudBees CD/RO server service |
|
CloudBees Software Delivery Automation server service principal name |
|
CloudBees Software Delivery Automation server service account |
|
End-user account |
|
Configuring the Kerberos KDC
Before setting up your CloudBees Software Delivery Automation servers and web servers with SSO, Kerberos principals required for authentication must be configured with Active Directory.
| Administrator privileges are required for the following procedures. |
To configure the Kerberos KDC:
Creating a user account
To create a user account in the Active Directory:
-
Log into the domain controller as administrator.
-
Create an account with a username (for example,
bob) and password.An organization typically already has its end user set up in the Active Directory.
Creating service accounts
Service accounts are used to run the services for the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation server and the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation web server. You can run both services under the same account. For examples, refer to Identifying the Kerberos SSO components.
To set up these service accounts:
-
Sign in to the domain controller as administrator.
-
Create a new user with a username and a password.
-
Select User cannot change password and Password never expires.
Mapping the user accounts to service principal names
Kerberos service principals for the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation web server and CloudBees Software Delivery Automation server services need to be created and associated with the service user accounts in Active Directory. You can use one of the following options to perform this operation:
Option 1: Using Windows Active Directory users and computers
-
Log into the domain controller as administrator.
-
Open the Windows Active Directory Users and Computers tool.
-
Find the user account that you created (for example,
efweb-krbsvc). -
Open user properties and navigate to the Attribute Editor.
If the Attribute Editor does not appear in the UI, select and enable it.
-
Select the servicePrincipalName attribute.
-
Enter the value
HTTP/efwebserver.example.com@example.com, whereefwebserver.example.comis the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) for the web server node.When a load balancer is used for the web server, this value should be the FQDN of the load balancer.
-
Repeat these steps for the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation server to associate the user account
efserver-krbsvcto the service principalHTTP/efserver.example.com@example.com. -
Enable the web and CloudBees Software Delivery Automation servers to require AES256-SHA1: make sure the Active Directory service account has The account supports Kerberos AES 256 bit encryption account option configured as described in Windows Configurations for Kerberos Supported Encryption Type.
The configuration related to AES256-only encryption must be performed for each Active Directory domain account that has mapping to web/CloudBees Software Delivery Automation service principal name (SPN). This sets
msDS-SupportedEncryptionTypesto16. -
Verify
msDS-SupportedEncryptionTypesis16. Enter the command:get-aduser efwebserver -property msDS-SupportedEncryptionTypesThe output should appear similar to the following:
DistinguishedName : CN=efwebserver,OU=Users,OU=CORP,DC=corp,DC=example,DC=com Enabled : True GivenName : efwebserver msDS-SupportedEncryptionTypes : 16 Name : efwebserver ObjectClass : user ObjectGUID : 478cceb3-89f7-4da1-9b71-53e3ed0c1202 SamAccountName : efwebserver SID : S-1-5-21-3236939686-3975733939-3482413644-16648 Surname : UserPrincipalName : HTTP/ip-10-0-129-123.corp.example.com@CORP.EXAMPLE.COM
Option 2: Using the setspn utility
The setspn utility lets you manipulate Service Principal Names (SPNs) in Active Directory.
-
Associate the
Service Principal Namefor the web server to its service account by entering:C:\ setspn -s `HTTP/efwebserver.example.com@example.com` efweb-krbsvc -
Associate the
Service Principal Namefor the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation server to its service account by entering:C:\ setspn -s `HTTP/efserver.example.com@example.com` efserver-krbsvc
Generating a keytab file
Keytab files need to be generated for services provided by the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation server and the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation web server. It stores the encryption keys for the Kerberos Services Principals, for example, HTTP/ efwebserver.example.com@example.com for a web server. The service account’s password is used to encrypt the entries in this file.
If your test environment has two virtual IP (VIP) FQDNs, for example one for the web server load balancer and another for the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation server load balancer, create two Active Directory accounts to generate the two keytabs: one for the web server service principal name (SPN) and one for the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation Server SPN. Each SPN must be mapped to its own domain account.
|
Only one domain account is needed and the same keytab can be used for both the web and CloudBees Software Delivery Automation servers if:
|
To generate keytab files for the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation server and CloudBees Software Delivery Automation web server:
-
CloudBees Software Delivery Automation server: Create a keytab file for the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation server that stores the credentials or encryption keys for its Service Principal Name (
HTTP/efserver.example.com@example.com) that is associated with the service account (efserver-krbsvc).To create a keytab file, enter the following
ktpasscommand on the domain controller node, with administrative privileges:ktpass -princ HTTP/efserver.example.com@EXAMPLE.COM -mapuser EXAMPLE\efserver-krbsvc -pass password +setpass +setupn +dumpsalt -crypto AES256-SHA1 -ptype KRB5_NT_PRINCIPAL -out efserver.keytabThe password must match the one used to create the service account for the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation server.
-
Web server: Create a keytab file for the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation web server that stores the credentials or encryption keys for its Service Principal Name (
HTTP/efwebserver.example.com@example.com) that is associated with the service account (efweb-krbsvc).To create a keytab file, enter the following
ktpasscommand on the domain controller node with administrator privileges:ktpass -princ HTTP/efwebserver.example.com@EXAMPLE.COM -mapuser EXAMPLE\efserver-krbsvc -pass password +setpass +setupn +dumpsalt -crypto AES256-SHA1 -ptype KRB5_NT_PRINCIPAL -out efwebserver.keytabThe password must match the one used to create the service account for the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation web server.
-
The output from
ktpassshould look similar to the following:Targeting domain controller: WIN-MUCJF62AKDL.corp.example.com Using legacy password setting method Successfully mapped HTTP/ip-10-0-129-123.corp.example.com to efwebserver. Building salt with principalname HTTP/ip-10-0-129-123.corp.example.com and domain CORP.EXAMPLE.COM (encryption type 18). .. Hashing password with salt "CORP.EXAMPLE.COMHTTPip-10-0-129-123.corp.example.com". Key created. Output keytab to efwebserver.keytab: Keytab version: 0x502 keysize 105 HTTP/ip-10-0-129-123.corp.example.com@CORP.EXAMPLE.COM ptype 1 (KRB5_NT_PRINCIPAL) vno 4 etype 0x12 (AES256- SHA1) keylength 32 (0x30ac141c0204cfd497d2ee6ae23e59b788d5100c44062414d880e6179eb06b94)
|
Verifying the keytab file
Use this procedure to verify the keytab has the correct SPN, enctype, and kvno, based on your operating system.
-
Linux
/opt/cloudbees/sda/apache/bin/klist -e -k -K -t \ /opt/cloudbees/sda/apache/conf/efserver.keytabThe output from this command is similar to the following:
Keytab name: FILE:/home/ec2-user/mykeytabs/efserver.keytab KVNO Timestamp Principal ---- ------------------- ------------------------------------------------------ 4 01/01/1970 00:00:00 HTTP/ip-10-0-134-109.corp.example.com@CORP.EXAMPLE.COM (aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96) (0x6d4b8a4c98bb0b3b1cf7d79b5f2105c704f91995b7704e803d02315f18a17bde) -
Windows
"C:\Program Files\CloudBees\Software Delivery Automation\jre\bin\ktab" \ -l -e -t -k efserver.keytabVerify that
kvnoin the keytab matches the output from themsDS-KeyVersionNumbervalue in the PowerShell command:
get-aduser efserver -property msDS-KeyVersionNumber
Here is the sample output:
DistinguishedName : CN=efserver,OU=Users,OU=CORP,DC=corp,DC=example,DC=com Enabled : True GivenName : efserver msDS-KeyVersionNumber : 4 Name : efserver ObjectClass : user ObjectGUID : d9b49f30-2643-45d0-8b92-f8797e4f38ad SamAccountName : efserver SID : S-1-5-21-3236939686-3975733939-3482413644-16649 Surname : UserPrincipalName : HTTP/ip-10-0-134-109.corp.example.com@CORP.EXAMPLE.COM
Testing authentication and ticket granting
-
Sign in to the server hosting the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation web server as the web server service account.
-
Run the following commands:
export KRB5_TRACE=/tmp/debug.txt \ /opt/cloudbees/sda/apache/bin/kinit -k -t \ /opt/cloudbees/sda/apache/conf/efwebserver.keytab \ <web server Service Principal Name>For example:
export KRB5_TRACE=/tmp/debug.txt /opt/cloudbees/sda/apache/bin/kinit -k -t \ /opt/cloudbees/sda/apache/conf/efwebserver.keytab \ HTTP/ip-10-0-134-109.corp.example.com@CORP.EXAMPLE.COMIf the keytab exists and the host or service principal has been correctly added to it then
kinitreturns immediately, without requesting a password.The authentication is successful if a ticket-granting ticket is cached in a
/tmp/krb5*file, for example:/tmp/krb5cc_1000. This way you can verify that the account is not locked. -
When the above
kinitis successful, list the tickets in the Credential Cache using:/opt/cloudbees/sda/apache/bin/klistYou should see output similar to the following:
Ticket cache: FILE:/tmp/krb5cc_1000 Default principal: HTTP/ip-10-0-134-109.corp.example.com@CORP.EXAMPLE.COM Valid starting Expires Service principal 08/12/2020 01:36:31 08/12/2020 11:36:31 krbtgt/CORP.EXAMPLE.COM@CORP.EXAMPLE.COM renew until 08/13/2020 01:36:13
Troubleshooting
If kinit returns either of these errors:
`kinit: Password incorrect`
`kinit: Preauthentication failed while getting initial credentials`
Then, as described in Deploying a Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 based Samba Server in a Windows Active Directory Domain:
-
The current web server service account password in Active Directory may not match the one used when generating the keytab. This means you may not have used the
+setpassand+setupnoptions to set the password in thektpass -princcommand used to generate the keytab. -
There may be a problem with your system’s clock. Verify the date command returns a time correct to within 5 minutes of your
kdc. You can verify this with thentpdateutility command:sudo ntpdate -qu your_domain_nameIf the time difference is within 5 minutes, it is fine. The above example shows the offset was only 0.03 seconds. Otherwise, sync it with the
kdcusing:sudo ntpdate your_domain_name -
Check if you have duplicate SPNs registered in your domain by running the following command on the Domain Controller or the Windows machine that can administer Active Directory:
setspn -xIf duplicate SPNs are found for the SPN used for the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation service account, then delete them using the
setspn -Dcommand or contact your Domain Administrator to remove the duplicate ones.
Configuring Kerberos constrained delegation
Kerberos constrained delegation allows an application (in this case, CloudBees Software Delivery Automation services) to reuse the end-user credentials to access CloudBees Software Delivery Automation resources hosted on a different server. Delegation is not enabled by default in the Active Directory. This means that service accounts for the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation web server and server need to be set up and trusted for delegation.
Configuration details
-
Set the delegation for the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation web server keytab account user, for example
efweb-krbsvc, to Do not trust this user for delegation. -
Perform the steps in Configure Analysis Services for Kerberos constrained delegation.
-
On the Delegation tab, select Trust this user for delegation to specified services only, followed by Use Kerberos only.
-
Select Add to specify the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation server services for which this account is permitted to delegate credentials.
-
On the Add Services page, select Users or Computers.
-
On the Select Users or Computer page, enter the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation server service keytab user,
efserver-krbsvc. -
Select OK to accept the service account.
-
(Optional) Verify the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation web server service keytab account user,
efweb-krbsvc, is configured correctly for delegation to the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation Service SPN.
-
-
Run the query below to discover the users or computers trusted for constrained delegation with the PowerShell ActiveDirectory module:
Get-ADUser -Filter {(msDS-AllowedToDelegateTo -ne "{}")} \ -Properties \ TrustedForDelegation,\ TrustedToAuthForDelegation,ServicePrincipalName,\ Description,msDS-AllowedToDelegateTo-
For the specific CloudBees Software Delivery Automation web server service keytab user:
PS C:\> Get-ADuser <WebServer_Service_keytab _user> \ -properties * | Select-Object \ cn,sAMAccountName,servicePrincipalName,\ userPrincipalName,trustedForDelegation,\ trustedToAuthForDelegation,\ msDS-AllowedToDelegateTo,modifyTimeStamp
-
To enforce constrained delegation, the Active Directory maintains a list of the SPNs of the instances of services that a service running under a specific account is allowed to delegate, that is, to obtain service tickets that can be used for constrained delegation. This list of SPNs is stored in the new Active Directory msDS-AllowedToDelegateTo attribute of the computer and user accounts on computers that are running Windows Server 2008. When a Windows Server 2008 KDC processes a service ticket request by using the constrained delegation extension, the KDC verifies that the SPN of the target service is included in the list of SPNs in the msDS-AllowedToDelegateTo attribute.
Enabling Kerberos on the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation server
After Kerberos SSO is configured and service accounts and Service Principal Names are created in the Active Directory, you must enable Kerberos SSO on each CloudBees Software Delivery Automation server.
| The following procedure is applicable for CloudBees CD/RO web servers, v9.1 and later. |
To enable Kerberos on the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation server:
-
Run the following
ecconfigurecommand to enable Kerberos SSO on each CloudBees Software Delivery Automation web server node.-
Linux:
sudo ecconfigure --webCopyKeytabFile "/path/to/efwebserver.keytab" --webEnableKerberosConstrainedDelegation true -
Windows:
ecconfigure --webCopyKeytabFile "c:/path/to/efwebserver.keytab" --webEnableKerberosConstrainedDelegation trueThis performs the following:
-
Copies the specified
keytabfile to/opt/cloudbees/sda/apache/conf/efwebserver.keytabon the web server. -
Configures the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation web server for the constrained delegation mode.
-
Restarts the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation web server.
-
-
Copy the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation server keytab to the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation server nodes.
-
Linux:
cp efserver.keytab /opt/cloudbees/sda/conf/efserver.keytab -
Windows:
C:\ copy efserver.keytab “C:\ProgramData\CloudBees\Software Delivery Automation\conf\efserver.keytab”The CloudBees Software Delivery Automation server keytab file is hardcoded and has to be efserver.keytab. You cannot use any other filename.
-
-
Create the Active Directory provider in the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation server as described in Directory providers.
-
Set the filter to:
(&(|(userPrincipalName={0})(sAMAccountName={0})(sAMAccountName={1}))(objectClass=user)(!(objectClass=computer))(!(userAccountControl:1.2.840.113556.1.4.803:=2)))The User Name Attribute can be userPrincipalNameorsAMAccountNameand has no bearing on the User Search Filter.
-
-
Enable Kerberos SSO for the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation server.
-
From the command line:
/opt/cloudbees/sda/bin/ectool --server localhost setSsoConfiguration --enableSsoKerberos 1 -
From the UI:
-
From the CloudBees navigation, select CD/RO or Analytics.
-
From the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation main menu, select , and then select Kerberos SSO.
-
-
-
Restart the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation server.
Example Kerberos configuration file
Below is a minimal example of a Kerberos configuration file, /etc/krb5.conf, that must reside on all CloudBees Software Delivery Automation servers, web servers, and agents.
[libdefaults] default_realm = EXAMPLE.COM [realms] EXAMPLE.COM = { kdc = dc.example.com admin_server = dc.example.com default_domain = example.com } [domain_realm] .example.com = EXAMPLE.COM example.com = EXAMPLE.COM
where:
-
EXAMPLE.COM: the name of the realm -
example.com: the domain name
Verifying /etc/krb5.conf
-
Sign in to the server hosting the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation web server as the web server service account user.
-
Run the
/opt/cloudbees/sda/apache/bin/kinitcommand. -
Enter the password at the prompt.
Errors like the following indicate the /etc/krb5.conf file needs to be fixed:
-
Kinit: krb5 init_context failed: 22 -
Kinit: krb5_get_init_creds wrong realm
Configuring web browsers
This section specifies how to configure web browsers that are hosting CloudBees Software Delivery Automation web servers in your enterprise. Browsers must be enabled to send the Kerberos credential for authentication.
CloudBees Software Delivery Automation supports the following browsers:
Google Chrome
On Windows:
Chrome on Windows should use Internet Explorer settings. For instructions, refer to Microsoft Internet Explorer.
Ensure the registry on your machine is properly set up. The recommended way to configure a policy on Windows is by using a Group Policy Object (GPO). However, on machines that are joined to an Active Directory domain, policy settings may also be stored in the registry under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE or HKEY_CURRENT_USER in the following paths:
-
Software\Policies\Google\Chrome\AuthServerWhitelist = efwebserver.example.com -
Software\Policies\Google\Chrome\AuthNegotiateDelegateWhitelist = efwebserver.example.com
On macOS:
To configure Chrome for Kerberos on macOS, complete the following steps. The example below is for a user named bob :
-
Enter:
/usr/bin/defaults write /Users/bob/Library/Preferences/com.google.Chrome.plist AuthNegotiateDelegateWhitelist "efwebserver.example.com" -
Enter:
/usr/bin/defaults write /Users/bob/Library/Preferences/com.google.Chrome.plist AuthServerWhitelist "efwebserver.example.com" -
Sign out of your user account.
-
Sign back in, and run
kinit bob@example.com.This generates a Kerberos ticket on your computer.
-
Confirm by running the
klistcommand.The list of Kerberos tickets appears.
-
Shut down and restart Chrome.
For more information about Chrome setup for Kerberos, refer to Chrome and Kerberos Single Sign On.
Troubleshooting
Following are common problems with Kerberos setup on Chrome on macOS:
SSO sign-in no longer works
Follow the steps below:
-
Sign out of your user account and sign back in.
-
On macOS, enter
kinit bob@example.comand generate a ticket for thekrbtgtaccount again. -
Ensure that the Kerberos ticket is not expired on your local machine.
On macOS, run the
klistcommand and see the Kerberos ticket expiry information.
Microsoft Internet Explorer
To configure Internet Explorer for Kerberos:
-
Navigate to and select Custom Level.
-
Under , select Automatic logon only in Intranet zone.
-
Select OK.
-
On the Security tab, select Local Intranet, and then select Sites.
-
On the Sites popup window, select all options (this is the default).
-
Select Advanced, and then add the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation web server FQDN to your local intranet zone.
-
Select Add, and then select Close.
Mozilla Firefox
To configure Firefox for Kerberos:
-
Navigate to the configuration editor.
-
Select I accept the risk!.
The list of preferences appears.
-
Double-click the network.negotiate-auth.delegation-uris preference.
-
Enter the value for the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation web server FQDN. For example, enter
efwebserver.example.com. This preference lists the sites for which the browser may delegate user authorization to the server. -
Double-click the network.negotiate-auth.trusted-uris preference.
-
Enter the host or domain names, delimited by commas.
You can use a wildcard for domain names by prefixing them with a dot. For example, .example.com. For the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation web server FQDN, you can provide theefwebserver.example.comvalue for this preference. -
Select OK, and then close the browser window.
Managing access control
The access control functionality in CloudBees Software Delivery Automation determines who can modify the single sign-on configuration settings.
To configure access control:
-
From the CloudBees navigation, select CD/RO or Analytics.
-
From the CloudBees CD/RO or CloudBees Analytics main menu, select .
-
Select Access Control. The Access Control settings display.
-
Review and change Privileges and Inherited Privileges as needed.
Signing in to CloudBees Software Delivery Automation
To sign in, copy https://<webHostName>/flow/ into a browser window, then enter your CloudBees Software Delivery Automation web host name as the <webHostName>.
|
If you experience page redirect problems during SSO sign in, you can modify the
|
The sample sign-in page below is SSO-enabled with GSuite and Kerberos SSO. Your page may be enabled with other SSO identity providers, such as Okta.
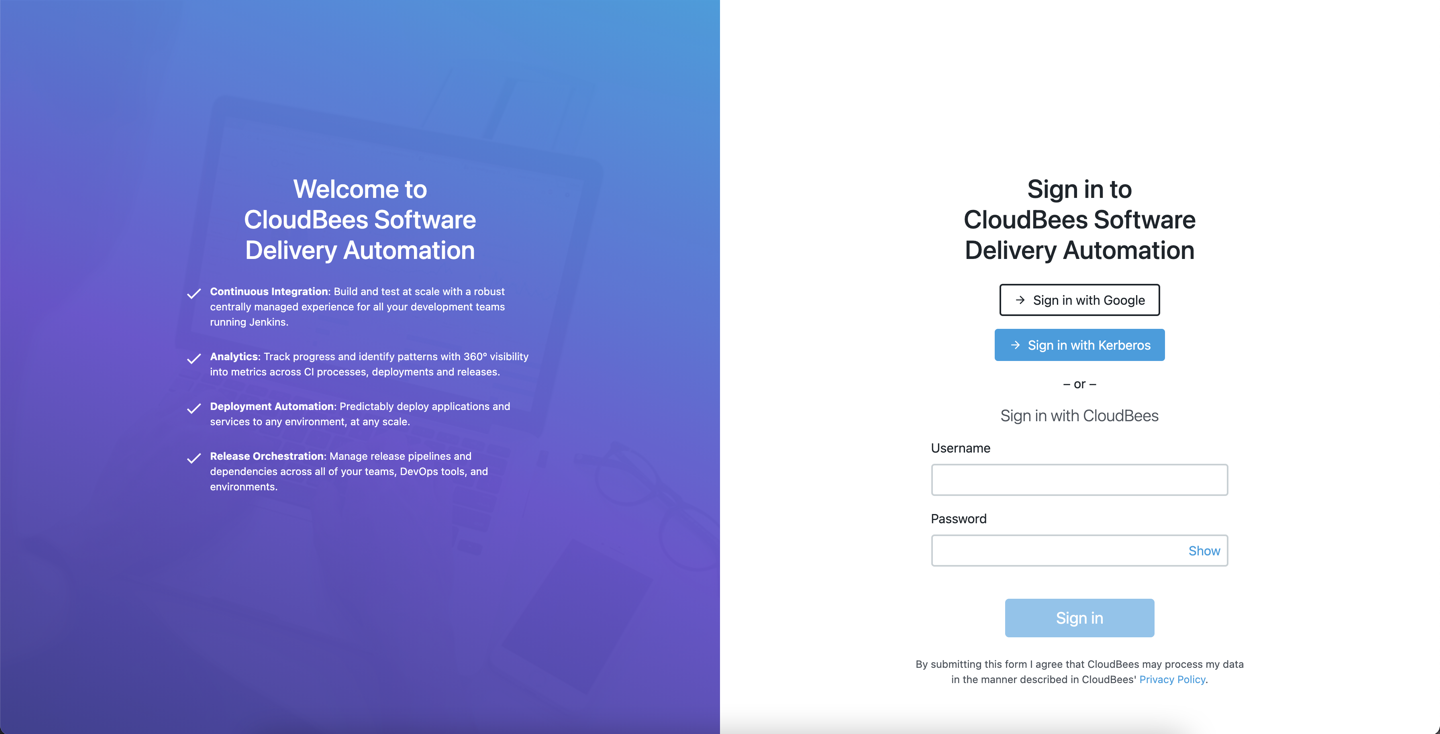
From here, use one of the following methods to sign in:
-
Select Sign in with Google: The credentials are authenticated via the Google identify provider, and if successful, you are redirected to the home page.
-
Select Sign in with Kerberos: This system has additionally been enabled with Kerberos SSO. The credentials are authenticated, and if successful, you are redirected to the home page.
-
Enter a Username and Password for local authentication. Then select Sign in. If successful, you are redirected to the home page.
| If you do not already have an active session, you are unable to sign in through the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation server when the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation server is being upgraded. The following message appears on the sign-in screen until the CloudBees Software Delivery Automation server upgrade is complete: “Server is starting. Please wait.” |