Depending on the scheme used to organize an operations center cluster, it may be necessary to copy artifacts from jobs that are on a remote client controller. For example, team responsible for QA may want to pull the artifacts to be tested from the development team’s server. To solve this class of problem the Operations Center Context plugin provides a build step and a pipeline step that can copy artifacts from another job, either on the root operations center or any client controller Jenkins instance in the operations center cluster.
|
The ability to copy artifacts across controllers within an operations center cluster has been added to operations center as an update to the 2.7.0.0 release. This functionality requires the following minimum plugin versions:
If individual controllers have not been upgraded then
|
| The CloudBees Secure Copy plugin is deprecated with support ending on September 1st, 2018. Users are encourage to use the Cluster-wide Copy Artifacts plugin as replacement. |
The Copy archived artifacts from remote/local jobs build step
This build step allows you to copy archived artifacts from a remote (or local) job.
To add the trigger just select the Copy archived artifacts from remote/local jobs option from the Add build step drop down.
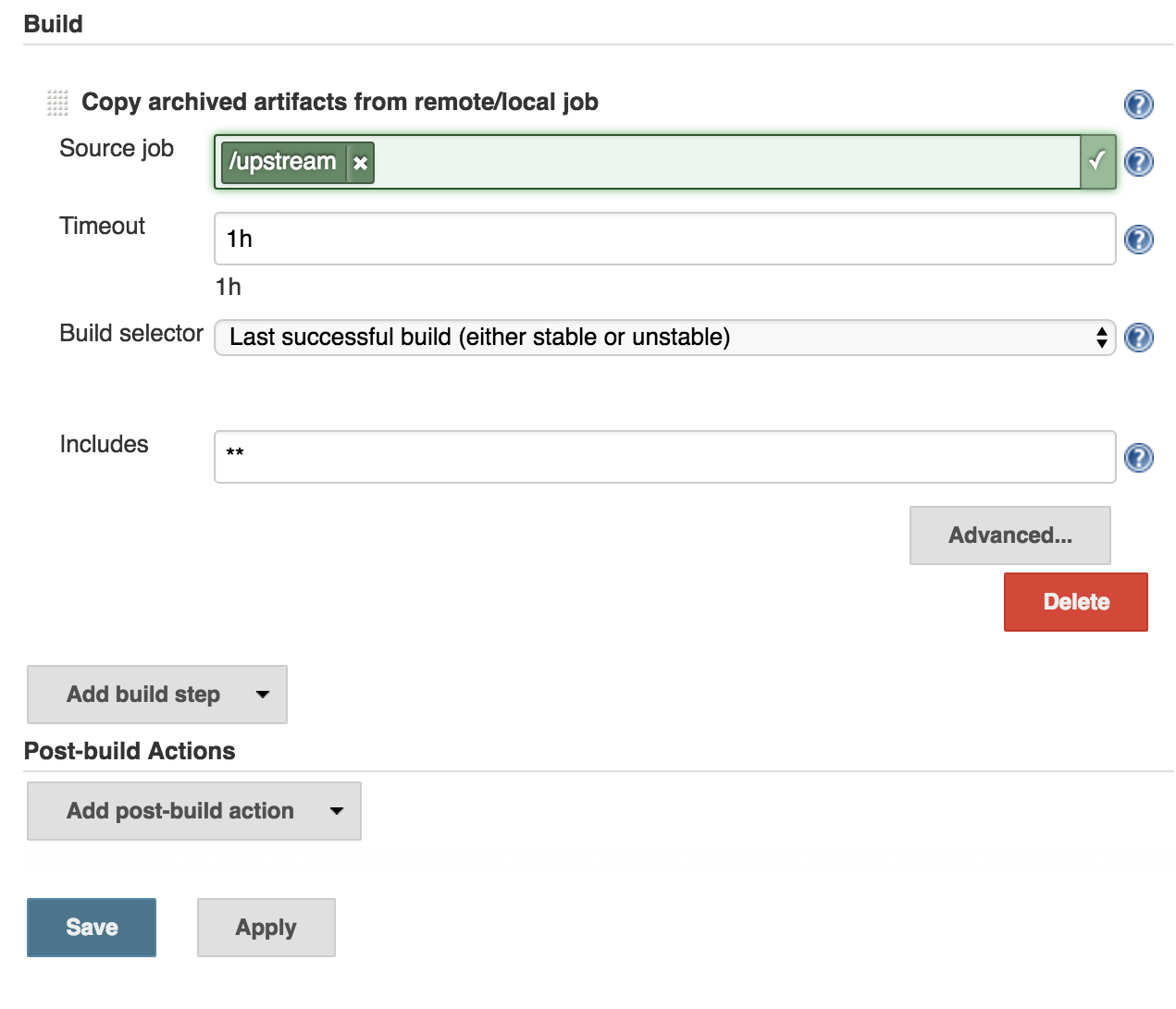
The main configuration options are:
- Source job
-
The job to copy. This uses the path browser UI component to allow you to navigate to the job you want to copy from.
- Timeout (
timeout) -
How long to wait for the artifacts to be copied. If no units of time are specified then the value is assumed to be in seconds. You can specify the timeout in multiple units and the semantics of those units will be preserved, e.g. 1h 65s will not be transformed into 3665s. The valid units are:
d,dayordaysdays
h,hr,hrs,hourorhourshours
m,min,mins,minuteorminutesminutes
s,sec,secs,secondorsecondsseconds
ms,milli,millis,millisecondormillisecondsmilliseconds
The following are all valid timeouts (though they will be simplified on save)
-
300i.e. 300 seconds -
5 minuteswill be simplified to 5m i.e. 300 seconds -
4 minutes and 60 secondswill be simplified to 4m60s i.e. 300 seconds -
3 minutes 120 secondswill be simplified to 3m120s i.e. 300 seconds -
45secs 3 minutes 75si.e. 300 seconds
Form validation in the snippet generator will display the simplified interpretation of the timeout
-
- Build Selector
-
How to select the build to copy artifacts from, such as latest successful or stable build, or latest "keep forever" build. Other plugins may provide additional selections. See the section on Build selectors for details of the specific implementations available.
- Includes
-
Relative paths to artifact(s) to copy or leave blank to copy all artifacts. This works just as a filter and doesn’t test whether all specified artifacts really exist. Check the
/artifact/browser of a build to see the relative paths to use here as the build page typically hides intermediate directories. You can use wildcards liketarget/checkout/**/target/*.zipand use comma to separate multiple entries. See the@includesof Apache Ant’s fileset for the exact format.May also contain references to build parameters like $PARAMor${PARAM}.
Additional behaviors of the build step can be controlled from the Advanced button.
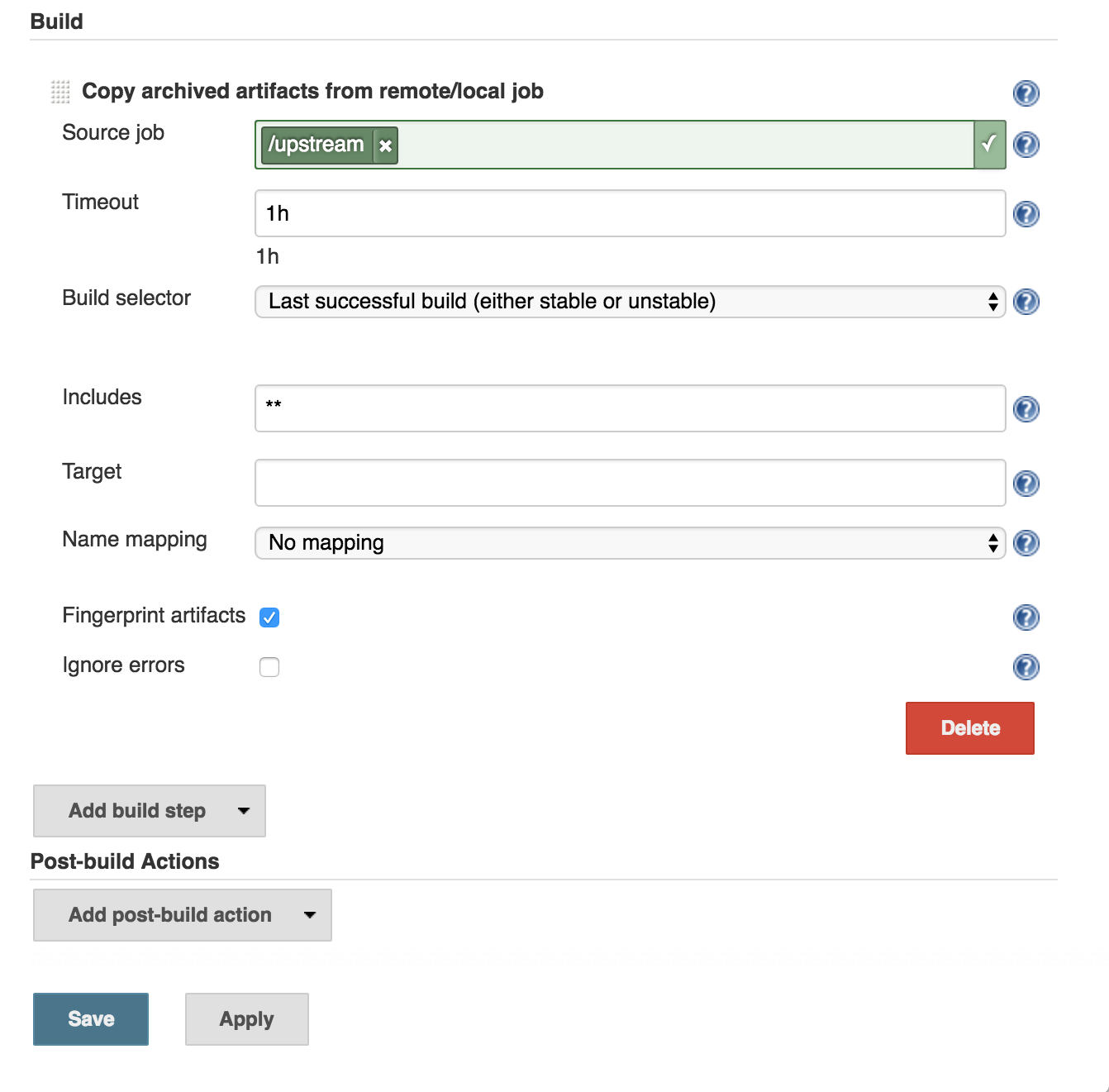
- Target
-
The directory to copy the artifacts into. Only paths within the workspace are supported.
- Name Mapping
-
Strategy that controls how artifact names are mapped when being copied. See the section on Artifact Name mappers for details of the specific implementations available.
- Fingerprint artifacts
-
Fingerprint the artifacts and associate with the build to enable the tracability features of Jenkins.
- Ignore errors
-
There are a number of possible error conditions:
-
The Jenkins controller containing the source job from which the artifacts will be copied may be off-line from operations center for longer than the timeout.
-
The Jenkins controller containing the target job into which the artifacts will be copied (i.e. this job) may be off-line from operations center for longer than the timeout.
-
The copying of the artifacts themselves may take longer than the timeout.
-
There are no matching files to be found in the source job.
-
There may be no builds available that match the configured build selector
-
The authentication that the target job is running as, after being mapped to an authentication on the source controller, may not have permission to see the source job or may not have permission to copy the artifacts from the source job
By default, if any of these issues are encountered, the target build result will be marked as a failure and the build stopped. Enable this option to ignore any such errors and continue the build.
-
There are two extension points that control the behavior of the build step:
Build selector
The build selector is a strategy for determining the build from which the artifacts should be copied.
There are ten strategies provided by the Operations Center Context plugin. The strategy is an extension point which enables other plugins to provide their own implementations.
|
Where possible use the strategies provided by the Operations Center Context plugin. If you are implementing a custom build selector strategy in a custom plugin, the strategy instance serialized and sent to the remote controller over a remoting channel that does not load classes from the sender. This means that if you want to use a custom strategy not provided by the Operations Center Context plugin you must ensure that the plugin providing the custom strategy is installed on all controllers that jobs will be copied between. |
The built-in strategies are:
| Last successful build |
This strategy will find the most recent completed build with a status of either Stable or Unstable. |
||
| Last stable build |
This strategy will find the most recent completed build with a status of Stable. |
||
| Upstream triggering build |
This strategy will look at the causes of the job to determine if it has been triggered by the source job. The search will only include the graph of jobs on the controller. The search will match job triggering using either the Cluster-wide job triggers functionality provided by Operations Center Context or the regular Upstream causes built in to Jenkins itself. There is a configuration option to fall back to the last successful build if no upstream cause can be identified. It is possible that multiple builds of the same upstream job may have been coalesced into a single run of the job using this build step. By default, the highest triggering build number will be used, but this can be configured to pick the lowest triggering build number instead. |
||
| Build identified by number |
This strategy will pick the exact specified build number only.
|
||
| Last build |
This strategy will pick the most recent build of the source job.
|
||
| Last completed build |
This strategy will pick the most recent completed build of the source job.
|
||
| Last failed build |
This strategy will pick the most recent failed build of the source job.
|
||
| Last unstable build |
This strategy will find the most recent completed build with a status of Unstable. |
||
| Last unsuccessful build |
This strategy will pick the most recent non-stable build of the source job.
|
||
| Build identified by a permalink |
This strategy will pick the most recent build returned by one of the source job’s permalinks.
|
Artifact name mapper
The artifact name mapper is a strategy for deciding the names of the artifacts when they are copied.
There are three strategies provided by the Operations Center Context plugin. The strategy is an extension point which enables other plugins to provide their own implementations.
|
Where possible use the strategies provided by the Operations Center Context plugin. If you are implementing a custom artifact name mapper strategy in a custom plugin, the strategy instance serialized and sent to the remote controller over a remoting channel that does not load classes from the sender. This means that if you want to use a custom strategy not provided by the Operations Center Context plugin you must ensure that the plugin providing the custom strategy is installed on all controllers that jobs will be copied between. |
The built-in strategies are:
| No mapping |
This strategy will use the path name that the artifacts were archived with. |
| Flatten all directories from name |
This strategy will strip the path component from the path name that the artifacts were archived with and just use the artifact base name. |
| Remove leading directories from name |
This strategy takes a parameter which is the number of directory segments to remove from the path name. If the archived artifact has less directory segments than the number to remove then the artifact’s base name will be used. |
The Copy archived artifacts from remote/local jobs pipeline step
The Operations Center Context plugin adds a pipeline step for copying artifacts from remote / local jobs: copyRemoteArtifacts.
The build step returns a list of strings corresponding to the names of the files that were copied.
In most cases the default options will be sufficient and the step can be invoked as:
copyRemoteArtifacts stepnode { copyRemoteArtifacts 'jenkins://cafebabedeadfeefcafebabedeadfeef/path/to/job' }
To control where the artifacts are copied, just wrap the copyRemoteArtifacts step in a dir step, e.g.
node { dir ("subdir") { copyRemoteArtifacts "jenkins://cafebabedeadfeefcafebabedeadfeef/path/to/job" } }
Similarly, errors can be ignored by wrapping using the standard idioms for pipeline scripts.
For more advanced control of options, it is recommended to generate the configuration using the snippet generator.
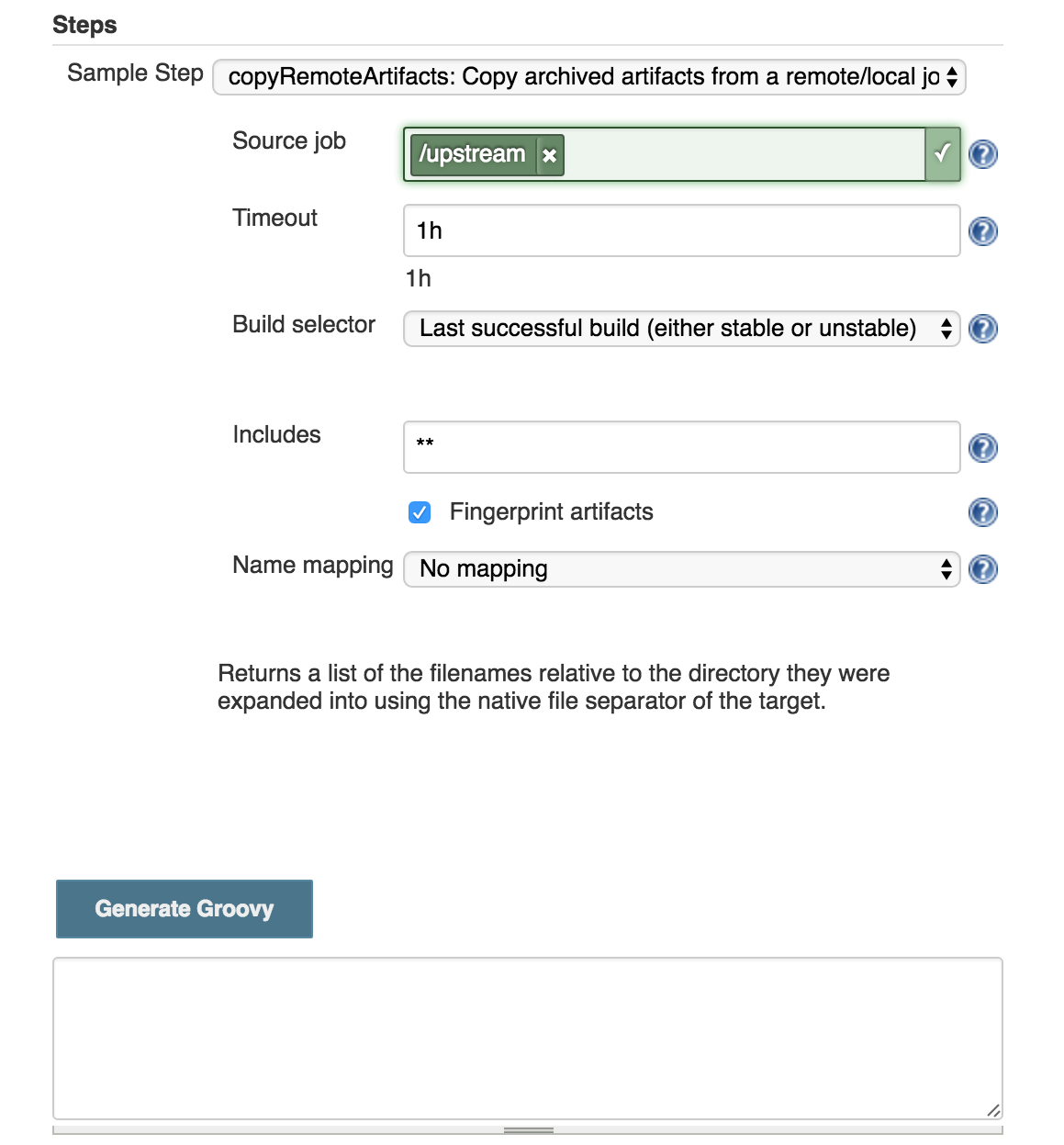
copyRemoteArtifacts step.The configuration options are:
- Source job (
from) -
The job to copy from.
This is a string value which can be of type:
jenkins://instanceID/path-
jenkins://the prefix of the remote path URI schema. -
instanceIDthe Jenkins Instance ID of the remote instance where to trigger the job or.to indicate the current instance. -
paththe path to the item
or of type
cjp:///path/from/root/of/cjoc-
cjp://the prefix of the remote path URI schema. -
path/from/root/of/cjocthe walking path from the root of operations center
The CJP protocol can only be used against a Trusted client controller. See Authentication mapping for more information.
-
- Timeout (
timeout) -
How long to wait for the artifacts to be copied. If no units of time are specified then the value is assumed to be in seconds. You can specify the timeout in multiple units and the semantics of those units will be preserved, e.g. 1h 65s will not be transformed into 3665s. The valid units are:
d,dayordaysdays
h,hr,hrs,hourorhourshours
m,min,mins,minuteorminutesminutes
s,sec,secs,secondorsecondsseconds
ms,milli,millis,millisecondormillisecondsmilliseconds
The following are all valid timeouts (though they will be simplified on save)
-
300i.e. 300 seconds -
5 minuteswill be simplified to 5m i.e. 300 seconds -
4 minutes and 60 secondswill be simplified to 4m60s i.e. 300 seconds -
3 minutes 120 secondswill be simplified to 3m120s i.e. 300 seconds -
45secs 3 minutes 75si.e. 300 seconds
Form validation in the snippet generator will display the simplified interpretation of the timeout
-
- Build Selector (
selector) -
How to select the build to copy artifacts from, such as latest successful or stable build, or latest "keep forever" build. Other plugins may provide additional selections. See the section on Build selectors for details of the specific implementations available.
- Includes (
includes) -
Relative paths to artifact(s) to copy or leave blank to copy all artifacts. This works just as a filter and doesn’t test whether all specified artifacts really exist. Check the
/artifact/browser of a build to see the relative paths to use here as the build page typically hides intermediate directories. You can use wildcards liketarget/checkout/**/target/*.zipand use comma to separate multiple entries. See the@includesof Apache Ant’s fileset for the exact format. - Name Mapping (
mapper) -
Strategy that controls how artifact names are mapped when being copied. See the section on Artifact Name mappers for details of the specific implementations available.
- Fingerprint artifacts (
fingerprint) -
Fingerprint the artifacts and associate with the build to enable the tracability features of Jenkins.
Tips and tricks
This section details some specific use cases and the recommended solutions for implementing them using the cluster-wide copy artifacts functionality.
Matrix to Matrix copying
I have two matrix jobs. Both matrix jobs have the same axes configurations. I want to copy the artifacts produced by the first job into the second job. I only want to copy the artifacts produced by the matching axes.
We will suppose there are two axes: the operating system and the CPU architecture.
The Operating System is the first axis with name OS.
The CPU architecture is the second axis with name ARCH.
We want to configure the test job to copy artifacts from the build job.
We want to copy:
* the OS=linux,ARCH=i386 artifacts to OS=linux,ARCH=i386
* the OS=linux,ARCH=x86_64 artifacts to OS=linux,ARCH=x86_64
* the OS=win,ARCH=i386 artifacts to OS=win,ARCH=i386
To do this, we need to:
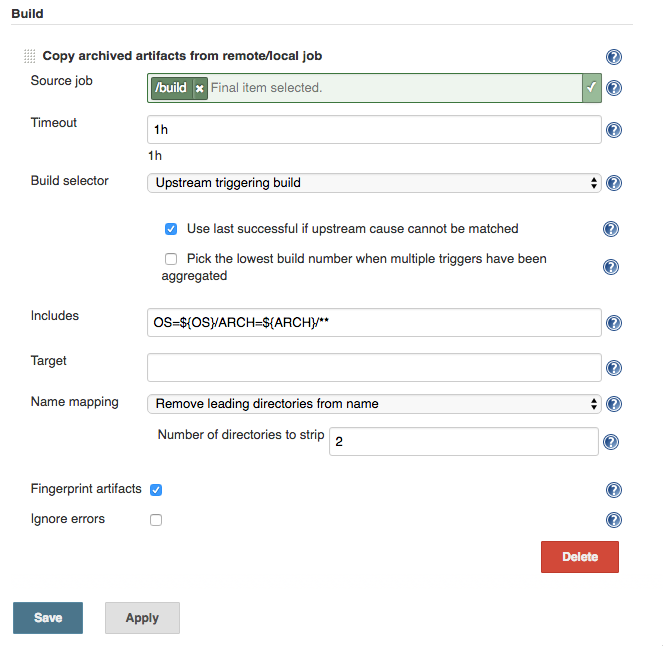
-
Select the matrix aggregator for the
buildas the source -
Specify the include pattern with the prefix
OS=${OS}/ARCH=${ARCH}/. For example instead of the*.zipwe would useOS=${OS}/ARCH=${ARCH}/*.zip. -
Specify the Remove leading directories from name artifact name mapping strategy with
2directories to be stripped - because we have two axes.
Coping Maven Job type artifacts
I want to copy the automatically archived artifacts from a multi-module Maven job type build.
The automatically archived artifacts from a multi-module Maven job type are exposed using the following path scheme: groupId/artifactId/ where groupId is the groupId of the module and artifactId is the artifactId of the module.
The file names are the file names used by the Maven job type when archiving the files in each individual module.