CloudBees CD/RO installation on Kubernetes uses internal services within the cluster to communicate between components, which ensures that communication within the cluster is efficient and secure. A common method for deploying CloudBees CD/RO on Kubernetes is to install CloudBees CD/RO components inside the Kubernetes cluster while installing worker agents such as deployment targets outside the cluster, such as on VMs and traditional platforms.
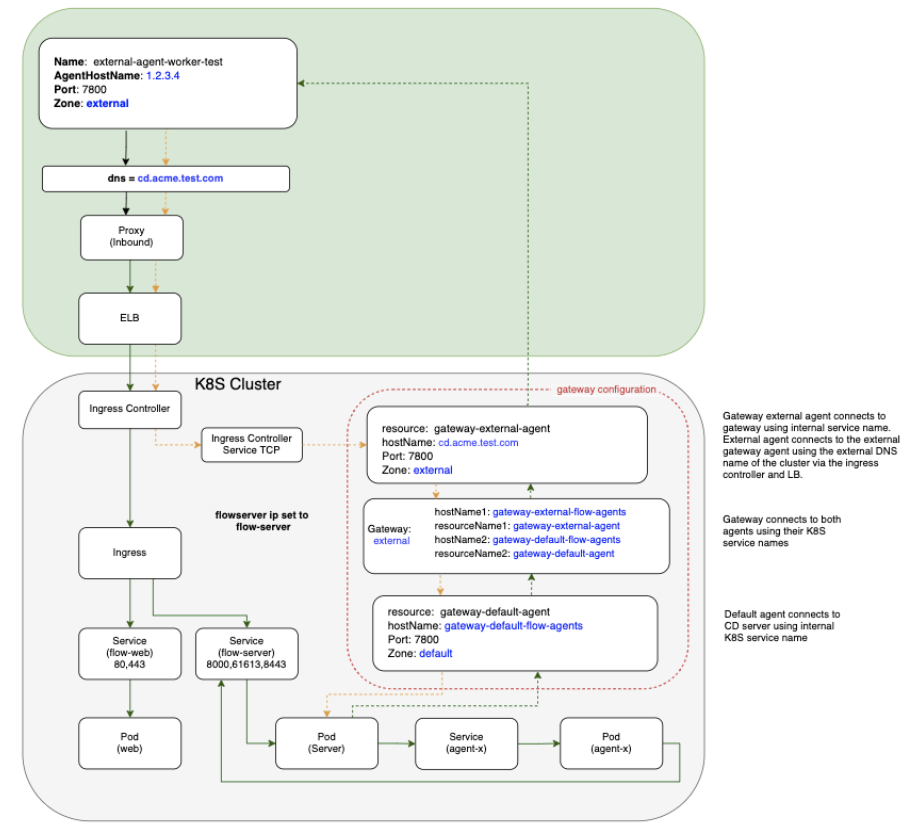
In a mixed inside and outside deployment use case, communications with the CloudBees CD/RO components happen with internal services installed on Kubernetes, while communication with CD agents happen outside the cluster. These external agents can communicate with the internal components using a pair of gateway agents.
Gateway agent pairs can be installed using one of these methods:
-
Using the CloudBees CD/RO Helm chart
-
Using the CloudBees CD/RO agent Helm chart
Installing gateway agent pairs using the CloudBees CD/RO Helm chart
-
Enable both
internalGatewayAgentandexternalGatewayAgentto enable the CloudBees CD/RO chart to install the agent sub-chart as gateway agents. Make sure you setingress.hostandexternalGatewayAgent.service.publicHostNameboth as the same value:ingress: host: my-flow.example.com internalGatewayAgent: enabled: true externalGatewayAgent: enabled: true service: publicHostName: my-flow.example.com -
Ensure your default values file has
nginx-ingress(Kubernetes versions 1.21 and earlier) oringress-nginx(Kubernetes versions 1.22 and later) tcp config map settings uncommented, to expose the 7800 gateway agents service:nginx-ingress or ingress-nginx: tcp: 8200: "{{ .Release.Namespace }}/flow-repository:8200" 8443: "{{ .Release.Namespace }}/flow-server:8443" 7800: "{{ .Release.Namespace }}/gateway-external-agent-flow-agents:7800" -
If you are not creating an ingress controller as part of the CloudBees CD/RO chart because you already have an existing ingress controller make sure you have
tcpconfigmap added to expose above ports and services (for more details, refer to the Kubernetes documentation):
helm repo add cloudbees https://public-charts.artifacts.cloudbees.com/repository/public/ helm repo update helm install releaseName cloudbees/cloudbees-flow \ -f valuesFile --namespace nameSpace --timeout 10000s
Installing gateway agents using the CloudBees CD/RO agent Helm chart
To create the gateway agent using the agent chart:
-
Create the server secret:
# Flow server credentials to use in order to register # with agent as a resource on the Flow server. kubectl create secret generic flow-agent-secret \ --from-literal=CBF_SERVER_USER='admin' \ --from-literal=CBF_SERVER_PASSWORD=<flow-server-password> \ -n <namespace> -
Create a values file for the internal agent called
gateway-default-agent.yaml:resourceName: gateway-default-agent replicas: 1 flowCredentials: existingSecret: flow-agent-secret service: publicHostName: gateway-default-agent-flow-agents -
Install the gateway internal agent using
gateway-default-agent.yaml:helm install gateway-default-agent cloudbees/cloudbees-flow-agent \ -f gateway-default-agent.yaml -n <namespace> -
Create a values file for the external agent called
gateway-external-agent.yamlthat addszoneName,publicHostNameand gateway configuration:resourceName: gateway-external-agent zoneName: external service: # External DNS hostname that the external agents would use to communicate # with the external gateway agent publicHostName: my-flow.example.com # configure gateway using external gateway agent gateway: # configure gateway using this agent enabled: true # Name of the gateway to create name: external # Name of gateway agent to pair with as gateway resource 2 pairedResourceName: gateway-default-agent flowCredentials: existingSecret: flow-agent-secret -
Install the gateway external agent using
gateway-external-agent.yaml:helm install gateway-external-agent cloudbees/cloudbees-flow-agent \ -f gateway-external-agent.yaml -n <namespace>