Changes in the CloudBees Feature Management UI affect flag values on the client device, such as a mobile app, web app, or backend system. You can control these changes using flag update flow.
|
Stateless architecture CloudBees Feature Management uses a stateless architecture by default, which means that each SDK pulls a static JSON file from CloudBees Feature Management cloud storage. The CloudBees Feature Management stateless architecture includes the following advantages:
Note - CloudBees Feature Management uses Server Sent Event (SSE) to alert the SDKs to download a new JSON config file in response to any configuration changes, so all changes are propagated to the clients instantly upon modification. |
Client-side SDK update flow
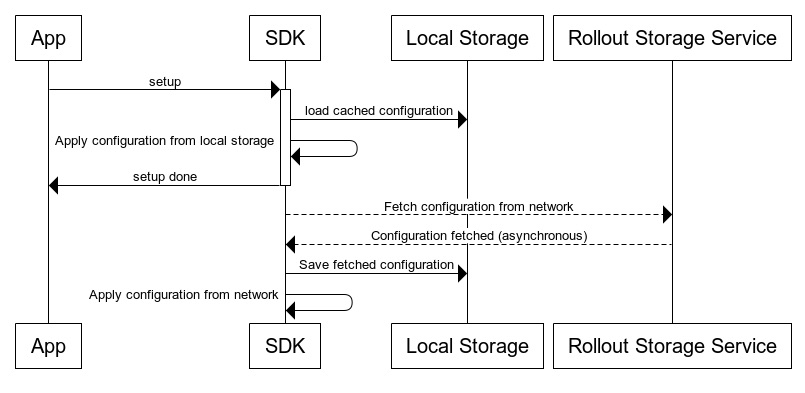
SDK setup flow
The client SDK setup flow operates in the following sequence:
-
Synchronous local storage fetching:
-
The application calls the Rox SDK setup function
-
The SDK checks for existing configuration in local storage
-
The configuration is applied synchronously
-
Setup function returns with all configured flags applied on the device
-
-
Asynchronous network fetching
-
In parallel to the local storage flow, an asynchronous network request is called from the SDK to the CloudBees Feature Management storage services
-
When the network request is returned:
-
Configuration is applied
-
Configuration is saved in local storage
-
-
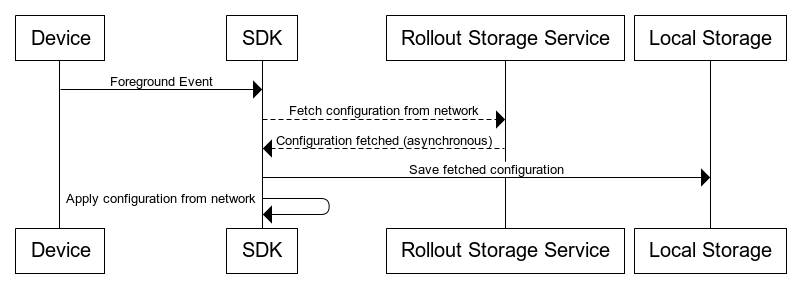
SDK foreground configuration fetching flow
When the SDK identifies a foreground event on clients such as mobile or TV, it triggers an asynchronous configuration fetching sequence to get a new configuration, if one exists, on CloudBees Feature Management servers.
| Refer to Understanding a flag freeze for more information. |
Server-side SDK update flow
Server-side SDKs fetch a new configuration file periodically. Various settings for each SDK are listed below:
| SDK | Default (in seconds) | Minimum (in seconds) | Additional notes |
|---|---|---|---|
JVM |
60 |
30 |
|
.NET |
60 |
30 |
|
Node.js |
60 |
30 |
|
JS SSR |
60 |
30 |
|
Python |
60 |
30 |
|
Go |
60 |
30 |
The optional parameter type is |
PHP |
30 |
30 |
PHP differs from other server-side SDKs in that it is not a live server, but a cache on the storage with a strategy that expires every 30 seconds. CloudBees Feature Management uses |
C |
60 |
30 |
There is an additional |
C++ |
60 |
30 |
There is an additional |
To change the default time frame, use FetchInterval / fetchIntervalInSec at the RoxOptions object. Refer to the following example:
RoxOptions options = new RoxOptions.Builder() .withFetchIntervalInSeconds(50) .withVersion("1.2.0") .build(); Rox.setup(this, options);
RoxOptions options = new RoxOptions(new RoxOptions.RoxOptionsBuilder{ Version = "1.0.4", FetchInterval = 60 }); await Rox.Setup(appKey, options);
Rox.register('', container); const options = { version: '2.0.0', fetchIntervalInSec: 60 }; Rox.setup(ROLLOUT_KEY, options);
from rox.server.rox import Rox from rox.server.rox_options import RoxOptions # setup configuration_fetched_handler in the options object options = RoxOptions( version="1.3.1" fetch_interval=60 ) cancel_event = Rox.setup('<key>', options).result();
import ( "time" "github.com/rollout/rox-go/v5/server" "github.com/rollout/rox-go/v5/core/model" ) var rox *server.Rox func setupRollout() { options := server.NewRoxOptions(server.RoxOptionsBuilder{ Version: "2.0.0", FetchInterval: time.Minute }) rox = server.NewRox() }
use Rox\Server\Rox; use Rox\Server\RoxOptions; use Rox\Server\RoxOptionsBuilder; $roxOptionsBuilder = (new RoxOptionsBuilder()) ->setVersion("2.0.0") ->setConfigFetchIntervalInSeconds(60); Rox::setup(ROLLOUT_KEY, new RoxOptions($roxOptionsBuilder));
#include <rox/server.h> RoxOptions *options = rox_options_create(); rox_options_set_fetch_interval(options, 60); rox_setup(DEFAULT_API_KEY, options);
#include <roxx/server.h> Rox::Options *options = Rox::OptionsBuilder() .SetFetchInterval(60) .Build(); Rox::Setup(DEFAULT_API_KEY, options);
Configuration fetched handler
Refer to Configuration fetched handler for how to identify when the SDK has loaded the configuration from local storage or the network.