This section shows how pipelines are represented in the CloudBees Flow UI. All of the information described in the previous sections is summarized in the pipeline definition in the Pipelines List.
Pipelines List
The Pipelines List shows all the pipelines that you have permission to view. To open it from the Home page (https://<cloudbees-flow-server>/flow), click Pipelines > All Pipelines.
This is a Pipelines List:
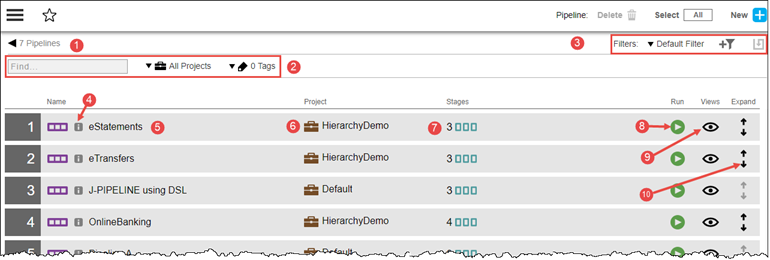
Each row in the list is a pipeline definition , consisting of the pipeline name, the project to which the pipeline belongs, and the number of stages in the pipeline. Selecting All or None and then clicking the Delete button removes the selected pipelines from the list. Clicking the blue + button in the upper right corner adds a pipeline.
1 |
Breadcrumb identifying the object you are viewing and the total number of pipelines. |
2 |
Default filter criteria—Configure the default filter here. See Searching and Filtering for filter details; see Object Tags for configuring tags. The default is to show the applications and microservices for all projects. To see only the objects for a specific project, click the down arrow in the All projects field and then select one or more projects in one of these ways:
If there are no matches, a message appears stating that there are no resource templates in the selected projects. |
3 |
Filter selector: select the filter to use on this page. Create custom filters here; see Searching and Filtering for details. |
4 |
Help button: click to show information about the object. |
5 |
Name of the pipeline. |
6 |
The project to which the pipeline belongs. |
7 |
Number of stages in the pipeline. |
8 |
Run button: click to run the pipeline. |
9 |
View button:click to select the Pipeline Editor. |
10 |
Expand button: click to view previous pipeline runs. |
The Pipeline Editor
Click on a pipeline in the pipeline object list opens it in the pipeline editor, providing a task-centric representation of the selected pipeline. This view option provides you the step-by-step details of the pipeline within the context to let you:
-
See a birds-eye view of the sequence of all tasks.
-
Make all edits from an optimized, single-view UI.
In the pipeline editor, you can author and edit a pipeline as well as view the underlying platform-level details. Consider the following pipeline with two stages: Dev and QA:
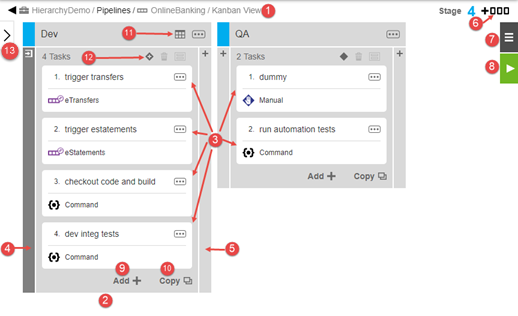
You can perform these actions:
-
Click the Add Stage button (6) to add a new stage to the pipeline.
-
Click the Object Menu button (7) to open a menu where you can get more details about the pipeline and take actions on the pipeline.
-
Click the Run button (8) to start a pipeline run.
-
In a stage, click the Add Task button (9) to open a dialog box where you can define tasks for the stage.
1 |
Breadcrumbs showing the object hierarchy, path to the pipeline, and the pipeline name. |
2 |
Stage in the pipeline, a milestone or checkpoint in the software delivery process. |
3 |
Tasks in the stage, which is the automation logic for a stage. See Tasks . |
4 |
Entry gate, consisting of the approvals to enter a stage. If a gate contains rules, it appears in gray and becomes expandable via mouse click so that you can view or edit the rules. If it has no rules, it appears in white (and is not expandable). In See Entry and Exit Gates . |
5 |
Exit gate, consisting of the approvals to exit a stage. If a gate contains rules, it appears in gray and becomes expandable via mouse click so that you can view or edit the rules. If it has no rules, it appears in white (and is not expandable). See Entry and Exit Gates . |
6 |
Add new stage button: click to add a stage. |
7 |
Object Menu button: click to open the object menu to get more details about the pipeline and to take actions on the pipeline.
|
8 |
Run button: click to run the pipeline. This initiates a pipeline run and opens the Pipeline Runs list showing the real-time progress of the pipeline run. You can also view the results of previous pipeline runs from here. |
9 |
Add Task button: click to create a new task from the beginning. |
10 |
Copy Task button: click to create a task by copying another task. |
11 |
Calendar button: click to view or set the start and end dates for this stage. This button appears only if there are start and end dates set. |
12 |
Stage Conditions button: click to view or set “run if” and “wait until” conditions and pipeline or release wait dependencies for this stage. |
13 |
Hierarchy menu toggle: click to slide open and to slide close the pipeline hierarchy menu. |
Creating and Managing Tasks
To create a task, click the Add Task button or the Copy button, then follow the prompts.
-
Enter a name for the task.
-
Click Select Task Type. The Task Type dialog box appears.
-
Native —List of standard task types such as Command or Application Process.
-
Plugins —The top ten plugins followed by the rest of the list. The ec_preferred_integrations property sheet determines the plugins to appear in this list and their order. For more information about property sheets, see Properties .
-
Frequently used plugins — The list of up to ten frequently used pipeline plugins. The ec_frequently_used_pipeline_plugins property sheet determines the plugins to appear in this list and their order.
-
It is populated by local plugin usage statistics collected by a watch dog thread run every five days. To change the watch dog schedule modify the Default background plugin statistics thread schedule server property via Settings on the Administration > Serve r page.
-
To manually modify this list, open the Automation Platform at https://<cloudbees-flow-server>/flow/, then select Administration > Server > ec_deploy > ec_frequently_used_pipeline_plugins, and then edit the list.
-
-
The rest of the list—to edit the list open the Automation Platform at https://<cloudbees-flow-server>/flow/and select Administration > Server > ec_deploy > ec_preferred_integrations t.
Click the task type. The dialog box closes, and the task now displays the selected task type.
-
-
Click Define. Add details for this task’s type. Subsequent dialog varies based on task type.
-
If you want to add another task, click Add + and repeat the previous steps to add it. The resulting task list shows the tasks in the order that they will be executed.