This content is available to customers with early access.
Use CloudBees platform role-based access control (RBAC) to define custom roles for managing feature flags, target groups, and custom properties. Permissions are evaluated at both the application and environment levels. To create, edit, approve, or deploy a flag or custom property, users must have the required permission for the application and environment.
Target groups are managed at the application level; however, applying a target group to a flag or rule in an environment, or updating a group that is referenced by a flag, requires the corresponding flag permissions in each affected environment.
Feature management permissions
Feature management actions, such as creating flags, managing target groups, or submitting approval requests, are controlled with specific permissions grouped into four categories. Depending on the action, required permissions may apply at the application level, the environment level, or both.
Approval request
-
Create,Update(approve), andDelete(reject or delete approval requests). Requires permissions at both the application and environment levels.
Custom property
-
Create,Update, andDeleteto manage custom properties used in targeting rules. Requires permissions at both the application and environment levels.
Flag
-
Create,Update, andDeleteto manage feature flags. Requires permissions at both the application and environment levels.
Target group
-
Create,Update, andDeleteat the application level. There is no environment-levelTarget grouppermission. -
If a target group is referenced by a flag configuration in one or more environments, updating or deleting that group may change flag behavior. In that case, the user must also have
Flag: Updatepermission at both the application and each affected environment. Applying or removing a target group in a flag rule also requiresFlag: Updatein that environment.
| New to role-based access control in CloudBees platform? Refer to Role-based access control for an overview of roles, permission levels, and scopes across the platform. |
Permission evaluation
When a user attempts a feature management action, CloudBees platform evaluates:
-
Assigned roles.
-
Permission levels within the relevant categories.
-
Role scopes at both the application and environment levels.
To successfully perform an action, the user must have the required permission at both scopes. If a permission is missing at either level, the action is denied.
For example, when a target group is referenced by a flag in an environment, updating that group requires the following:
-
Target groups:Updateat the application level. -
Flags:Updateat the application level and in each environment where the flag uses that group.
Assign feature management permissions
The following steps explain how to assign permissions to a custom role from the Roles screen in the UI.
-
Navigate to .
-
Select Create role.
-
Name the role (for example,
FM Admin).-
Select
 next to Custom role, and then enter the role name.
next to Custom role, and then enter the role name. -
Select
 next to Description to enter a short summary of granted permissions.
next to Description to enter a short summary of granted permissions.
-
-
Select: Feature management.
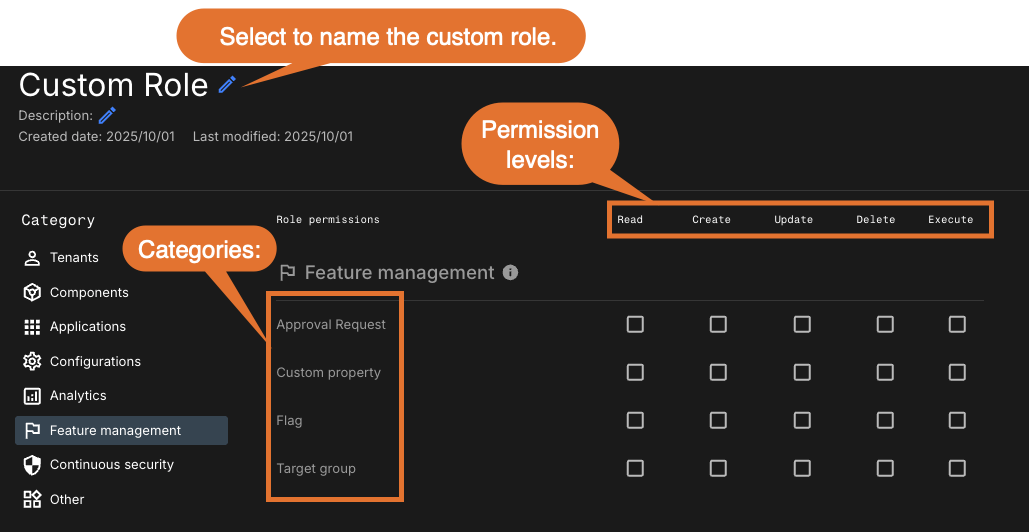
Permission levels for feature management
Permissions for feature management are assigned at the category level, using one or more permission levels.
| Level | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Grants read access to feature management entities (flags, target groups, and custom properties). Granted to all users by default. |
||
|
Allows users to create new flags, target groups, approval requests, or custom properties. |
||
|
Allows users to edit an entity. For example, to update a flag’s configuration or target group conditions.
|
||
|
Permits users to delete a flag, target group, or custom property. Also required to reject or delete an approval request. |
||
|
While |
View feature management permission categories and associated actions.
| Category | Possible permissions | What the permission allows | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Approval requests |
|
Submit, approve, or reject feature flag approval requests. |
||
Custom property |
|
Define and manage custom properties used in flag targeting rules. |
||
Flags |
|
Manage feature flags, including creating, updating, and deleting. |
||
Target groups |
|
Manage target groups at the application level.
|
Custom role examples for for common feature management use cases
Next, using the permission information from above, the examples that follow illustrate how to create custom roles for common feature management use cases.
Create an admin role
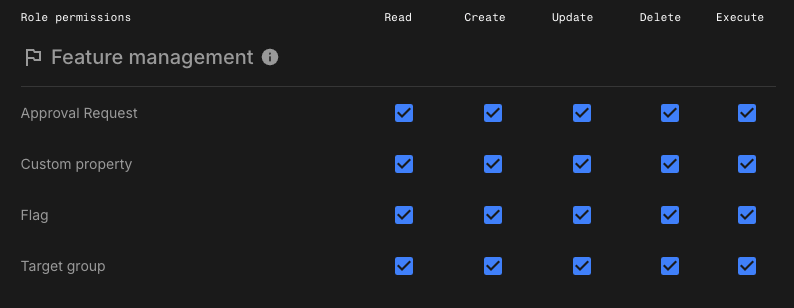
Use this example to set up a custom role for organization administrators who need full permissions for feature management capabilities. This custom role grants full control across all feature management categories, including approval requests, feature flags, target groups, and custom properties.
-
Follow the same [process_above], except for the permissions.
-
Apply the required permissions as shown in this example:
-
Approval request:-
Createto propose a request. -
Updateto approve a request. -
Deleteto reject or delete a request.
-
-
Flags:-
Create,Update, andDeleteto create, update, and manage flag settings.
-
-
Target group:-
Create,Update, andDeleteto manage audience targeting groups.
-
-
Custom property:-
Create,Update, andDeleteto manage flag rule conditions and context-based targeting.
-
-
-
Select Save.
-
To grant the role, go to .
Create a target group admin role
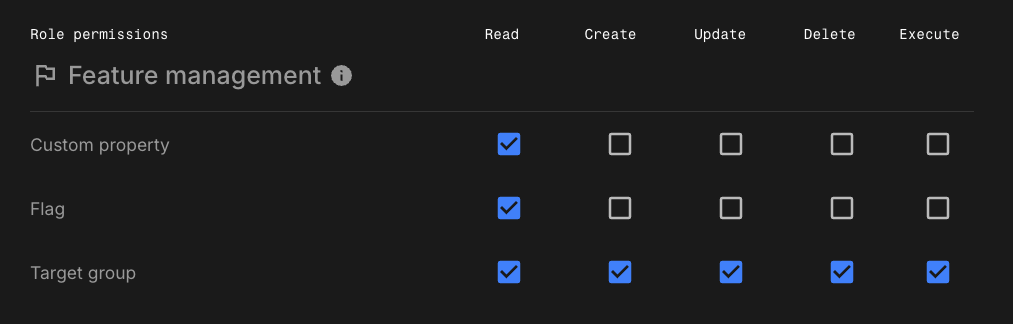
Use this role to grant permissions to a user or team responsible for managing audience targeting and rollout strategies.
-
Follow the same [process_above], except for the permissions.
-
Assign the following permissions:
-
Readmay be selected in the UI, but it is not required because all users are granted read access by default. -
Target group:Create,Update, andDeleteto manage targeting groups.
-
-
Select Save.
-
To grant the role, go to .
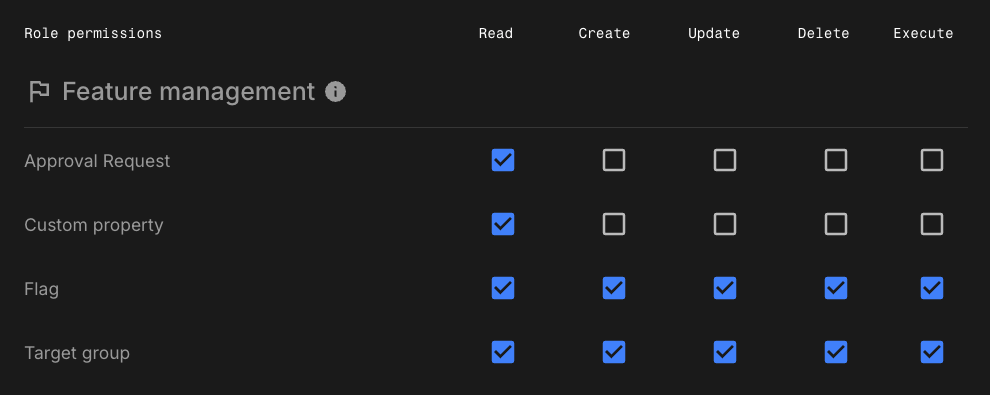
Adjusting target group permissions for environments
When target groups are referenced by flags in one or more environments, updating a target group may change flag behavior. To ensure proper functionality, the user must also have Flag permissions, typically Update or higher, at the application level and in each affected environment.
Flag permissionsCreate a flag owner role
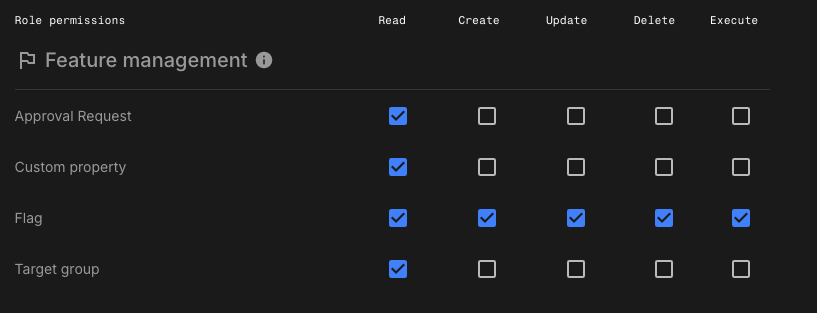
Use this role for users who are responsible for creating, managing, and deploying feature flags, but who do not need full access to approval requests, target groups, or custom properties.
-
Follow the same [process_above], except for the permissions.
-
Assign the following permissions:
-
Approval request:Read -
Custom property:Read -
Flag:Read,Create,Update, andDelete -
Target group:Read
-
-
Select Save.
-
To grant the role, go to .
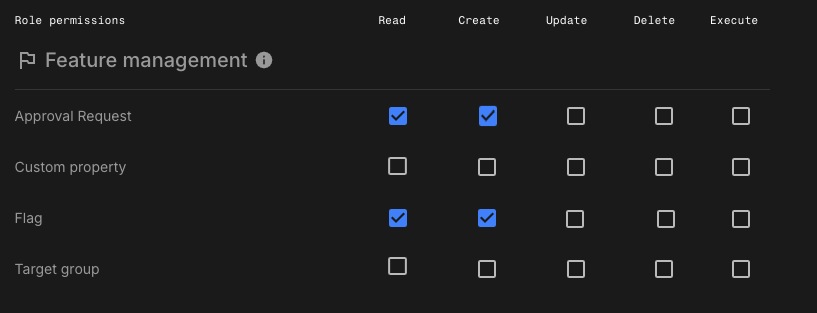
Create a flag contributor role (no save)
Use this role if you want users to draft feature flag changes without the ability to save them directly. This is useful for developers or team members who need to suggest flag edits but should not have permission to apply changes.
| Role | Feature management, Role permissions | Can propose approval? | Can approve/reject? | Can edit flag configuration? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Flag change requester |
|
-
Follow the same [process_above], except for the permissions.
-
Assign the following permissions:
-
Approval request:Read,Create -
Custom property: N/A -
Flag:Read,Create -
Target group: N/A
-
-
Select Save.
-
To grant the role, go to .
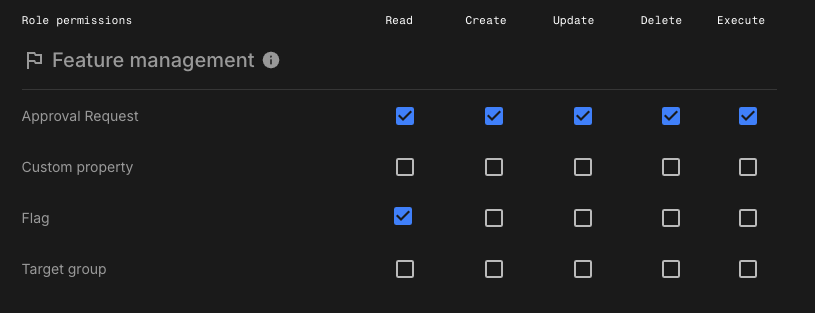
Create an approver role
Use this role to allow users to review flag changes and approve or reject them—but not modify flag configurations directly. This role is useful for team leads, product owners, or QA specialists who serve as reviewers during rollout.
| Role | Feature management, Role permissions | Can propose approval? | Can approve/reject? | Can edit flag configuration? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Flag approver |
|
-
Follow the same [process_above], except for the permissions.
-
Assign the following permissions:
-
Approval request:Read,Create,Update, andDelete -
Custom property:Read -
Flag:Read -
Target group:Read
-
-
Select Save.
-
To grant the role, go to .
For minimum permissions:
-
Updateis required to approve a request. -
Deleteis required to reject or delete a request.
CloudBees recommends assigning only the minimal permissions necessary for each user’s responsibility.
-
Assign roles at the application and environment scopes
The following examples illustrate how to assign roles across different scopes—organization, application, and environment.
Admin example
-
Flag name:
ImpressionsFlagAdmins -
Role:
fm_adminwith full feature management permissions -
Scope assignments:
-
Application:
fm-impressions-dev -
Environments associated with that application:
DevelopmentandLocal
-
Developer example
-
Flag name:
ImpressionsFlagsDevs -
Roles:
fm_adminand an organization-level role for general access -
Scope assignments:
-
Application:
fm-impressions-dev -
Environment:
Local
-
These examples demonstrate that users typically need both application, and environment-scoped role assignments to perform actions that impact features or behavior in a target environment.
Target groups are managed at the application level, but applying a target group to a flag or updating one that is referenced by a flag requires the appropriate Flag permission, specifically, Update, at the environment level.