An application in the CloudBees platform represents an entire software application, tying in multiple components, if desired. Use the application feature to create relationships in the platform that closely align with how your software is structured.
By definition, an application is a higher-level model for maintaining components in an organization. Because multiple components often work together to compose a complete piece of software, applications can be used to organize projects by the full software product being developed.
Use applications to configure software releases with CloudBees platform. For more information, refer to Releases.
Application features
You can use applications to:
-
Create a deployment process to orchestrate component deployment across multiple environments.
-
Utilize deployer workflows that automatically deploy all components based on the application manifest.
-
Visualize both direct and indirect dependencies (shared services).
-
Organize dependencies by execution, deployment, or semantic version.
-
Reference dependencies, but not actually deploy them, as part of the deployment.
-
Use approved flows, or "release templates".
-
Track release versioning, where each version is a collection of specific artifact versions and release process values.
-
Generate deployer workflows automatically based on application components using the assisted workflow creation feature.
View application details
You can view the applications in your organization by selecting Applications. Refer to Manage applications to learn more about how to access and manage applications in your organization. Select the Application name link next to the status icon to review detailed information for that application.
In the application details screen, use the tabbed navigation to access all the activities linked to an application.
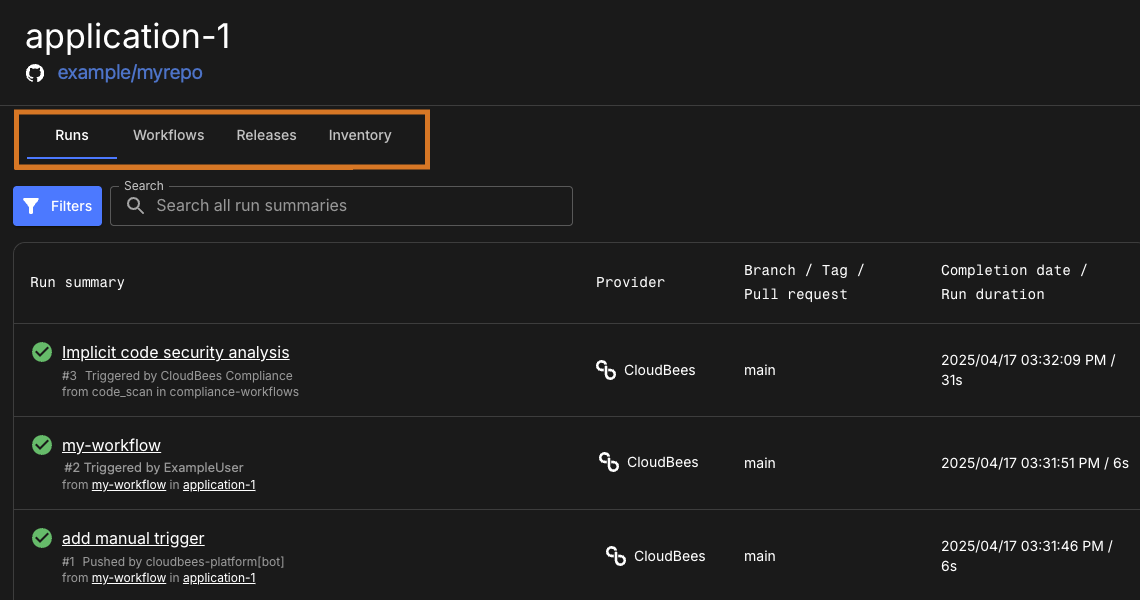
Each application tracks the setups and executions of its workflows through the Runs tab.
Runs
Review details of every workflow execution in an application on Runs. This view includes trigger information, links to the workflow composer, the run completion date, and the run duration.
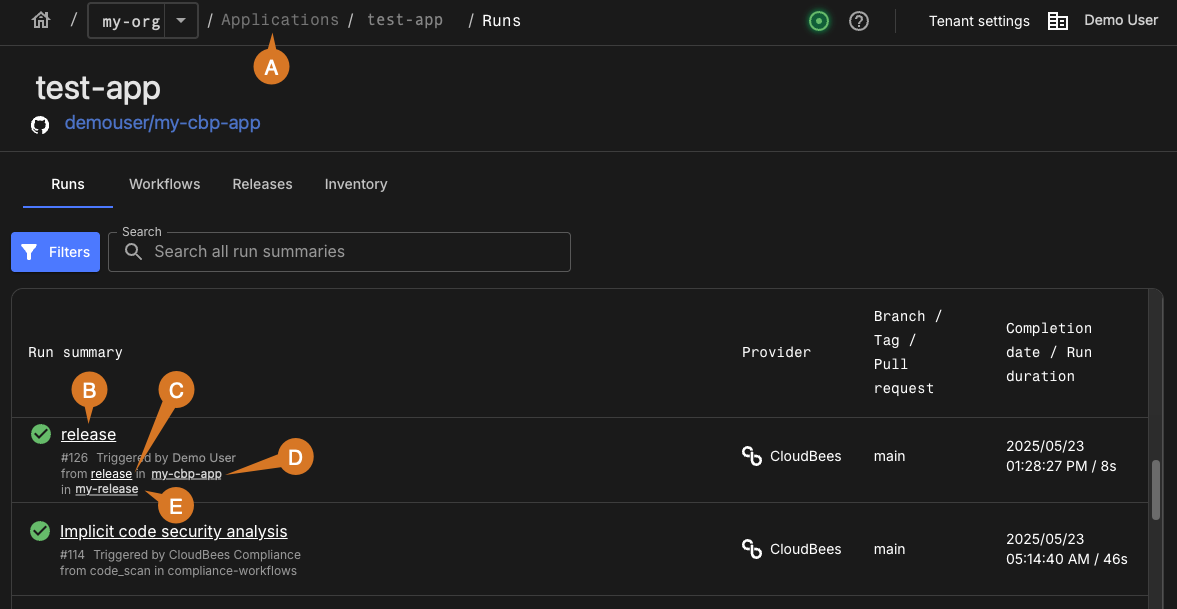
As in the above example, perform any of the following:
-
Select the applications list using the breadcrumbs.
-
View Run details for a workflow run:
-
Select the commit message for runs triggered through a pull request or a commit.
-
Select the workflow name for manually triggered runs or scheduled runs.
-
-
Select the workflow name to view and edit the workflow YAML file.
-
Select the component name to view the component summary.
-
Select the release, if present, to view release details.
To learn more, refer to Runs.
|
If you have implemented implicit security scanning, the analysis runs are available in this list, as shown in the example above. To learn more about configuring implicit security scans, refer to Manage security tools. Alternatively, view your application runs by:
The run summary for your application is displayed. Implicit security analyses are not included in this run list. |
Workflows
Automate software development tasks with CloudBees platform workflows, which are composed in YAML format.
Within a workflow:
-
Each task is considered a step within a job.
-
Jobs can run sequentially or in parallel.
-
Workflow files are defined and edited within each application.
In an application, you can create and manage the following types of workflows:
-
Standard workflows: Used for individual build or deployment processes. Often focused on a single component or environment.
-
Staged workflows: Organize complex release activities into stages, where each stage targets a specific environment (like staging or production).
-
Deployer workflows: Reusable workflows that deploy the appropriate set of components to an environment. These are typically called within staged workflows.
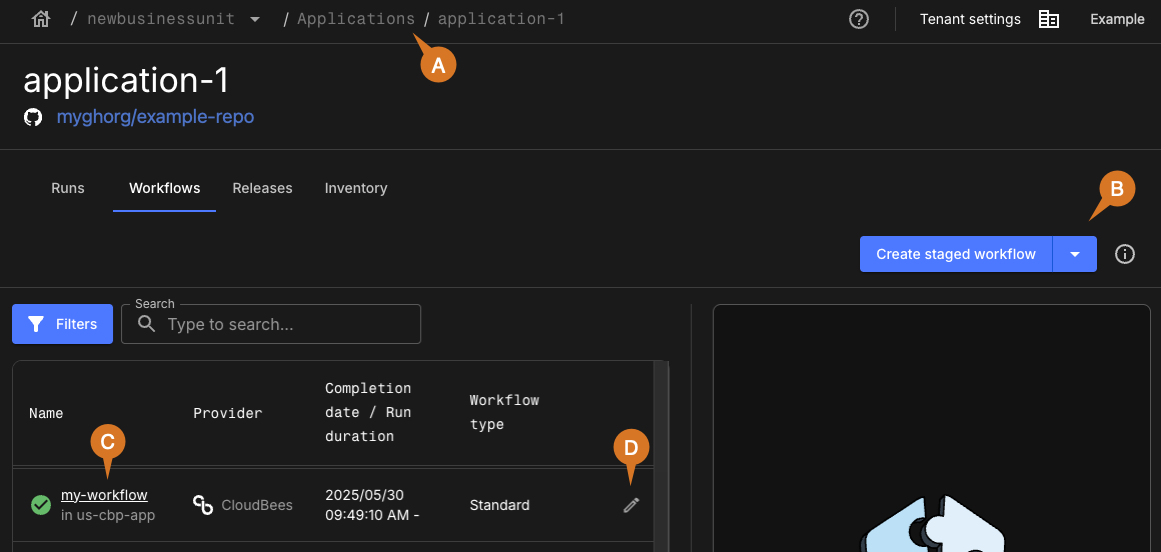
Explore and manage workflows as in the above example:
-
Select the applications list using the breadcrumbs.
-
Select
 to create a workflow.
to create a workflow. -
Select a workflow name to view the YAML file.
-
Select
 to edit the YAML file inline.
to edit the YAML file inline.
Standard workflows
Standard workflows let you define YAML-based tasks such as building an artifact, running tests, or deploying a component to a predefined environment. They execute sequentially unless specified with parallel or job dependencies.
Use these when you want to automate:
-
Build jobs for a single component
-
Environment-specific deployments
-
CI/CD steps for isolated services
Staged workflows
Staged workflows group release activities into structured stages. You typically use a staged workflow when you want to promote the same release through multiple environments; for example, dev > stage > prod, with clear checkpoints between each.
Each stage can contain its own tasks, and most importantly, calls a deployer workflow to handle deployment logic.
Stages rely on two key parameters when calling the deployer:
-
manifest: A JSON string specifying which component versions to deploy. -
environment: The destination environment for deployment.
Refer to:
Deployer workflows
Deployer workflows are reusable YAML files (deployer.yaml) that handle multi-component deployments across environments.
These workflows are called by staged workflows, not executed directly by users. When triggered with a manifest and environment, a deployer workflow:
-
Iterates across every component listed in the manifest.
-
Calls each component’s own
deploy.yaml. -
Passes in the artifact version and target environment.
-
Uses conditional logic (
ifstatements) to only deploy what’s needed.
| CloudBees platform provides an assisted creation experience when you don’t already have a deployer. For example, when starting a release workflow and no deployer exists, you’ll be prompted to generate one automatically. |
| If you change the components associated with an application, update your deployer workflow to reflect the correct component list. |
Refer to:
Releases
Manage the release of software to a live environment with a CloudBees platform application. Each release includes a workflow that orchestrates the release, the release manifest, and the metadata. Within application Releases, you can create and manage releases, monitor release statuses, and close and delete releases that are no longer needed.
Release workflows typically use a deployer workflow to deploy application components to different environments at each stage of the release. The deployer accepts a manifest (specifying which artifact versions to deploy) and an environment parameter, then orchestrates the deployment of all components to that environment.
|
When creating a staged workflow for a release, if no deployer workflow exists in the application, the platform prompts you to create one. The assisted creation feature generates a deployer workflow based on your application’s component associations, making it easy to set up a complete release process. |
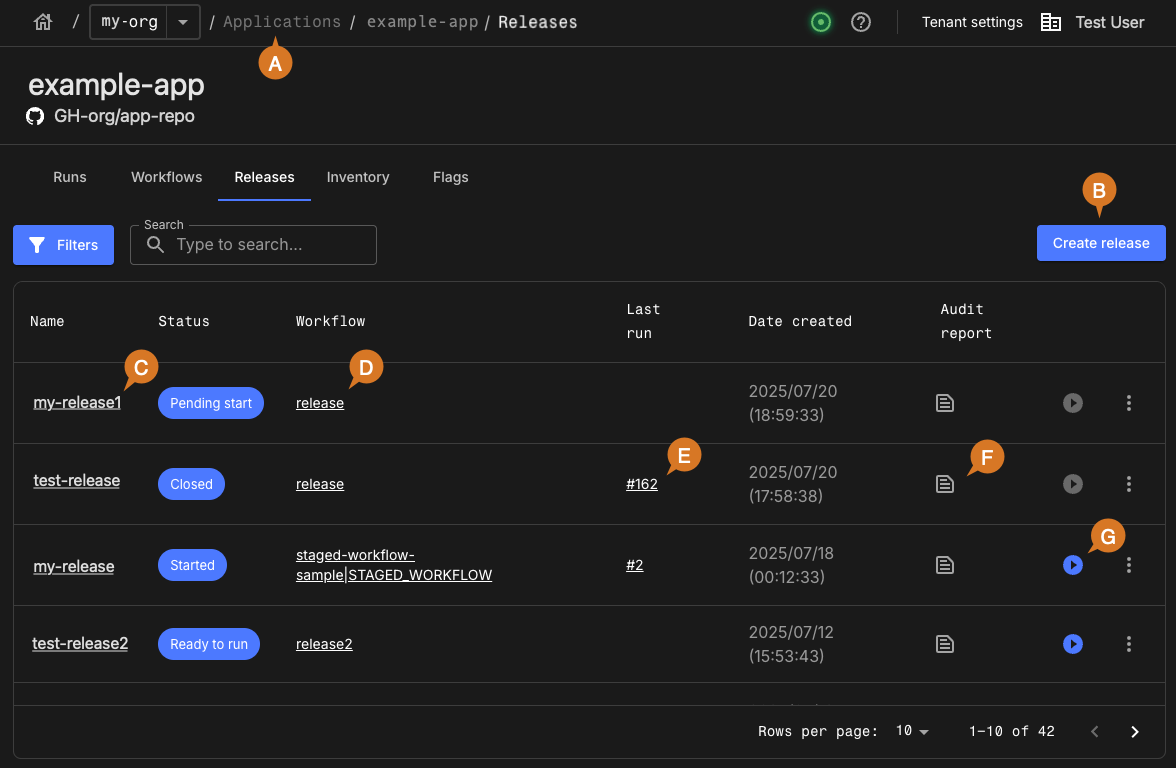
As in the above example, perform any of the following:
-
Select the Applications list using the breadcrumbs.
-
Select Create release to create a release.
-
Select the release name to view the release definition and runs summary.
-
Select the release workflow name to view and edit the workflow YAML file.
-
Select the run number to view the details for the last run, if the release is in Started or Closed status.
-
Select
 to view the audit report.
to view the audit report. -
Select
 to trigger a release workflow, if the release is in Ready to run or Started status.
to trigger a release workflow, if the release is in Ready to run or Started status.
For more information, refer to Releases.
View a real-time map of which artifacts are deployed across environments in the Inventory tab.
Inventory
If you have executed workflows to deploy artifact versions to infrastructure, track these deployments as environment inventory items. When deployments are part of an application release, these environment inventory items are associated with the application in its Inventory. The inventory displays where artifact versions of the application are currently deployed across all environments. Customize the view of the inventory by ordering, showing, and/or hiding any environments.
Artifacts are displayed only if they have been generated by running a workflow that has been configured to collect artifact data.
For more information, refer to:
View and manage the application environment inventory.
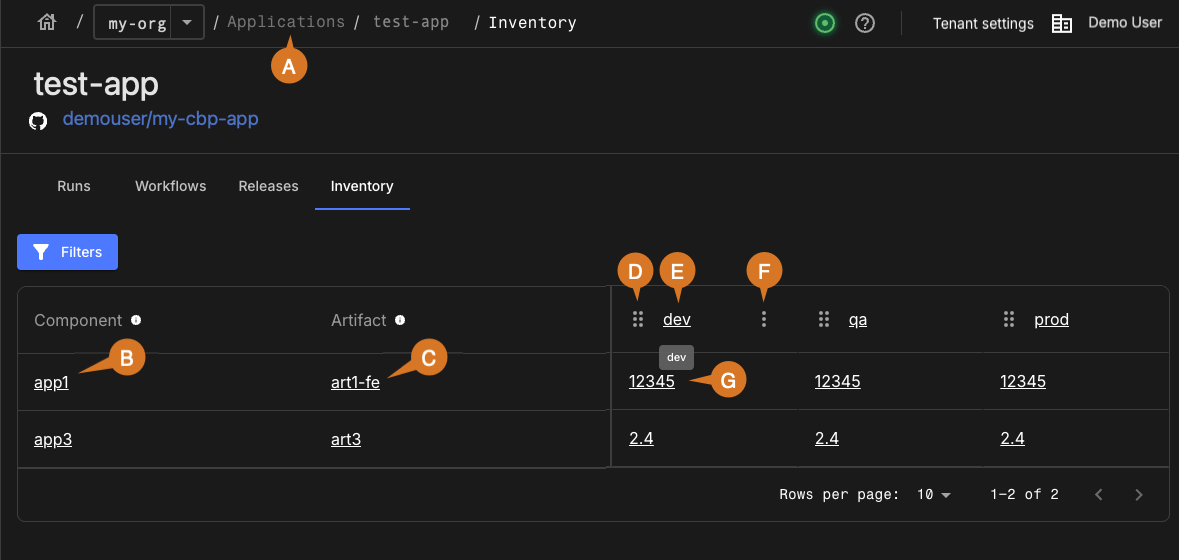
As in the above example, perform any of the following:
-
Select the Applications list using the breadcrumbs.
-
Select the component name to view the summary of the associated component.
-
Select the artifact name to view the current artifact version information.
-
Select
 to move an environment to a different column.
to move an environment to a different column. -
Select an environment to view all artifacts associated with that environment.
-
Hover over the Component header, the Artifact header, and the environment headers to manage column display: Select
 , and then select a Hide column or Manage columns option.
, and then select a Hide column or Manage columns option. -
Select the associated artifact version to view more details.
Application security
The application security overview dashboard provides application owners and security leaders with a continuous view of the latest security metrics. It can be used for reporting and review purposes, and greatly helps continuous security-posture management.
To access the application security overview dashboard:
-
Select an organization.
-
Select Applications, then select an application.
-
Select Security overview.
For further information on the application security overview, refer to Security overview