CloudBees Unify uses a YAML-based domain-specific language (DSL) to specify its workflows and to define reusable event-driven actions.
For convenience, the full list of all CloudBees Actions is displayed on the left menu pane. CloudBees actions provide the core functionality necessary for authoring workflows, including:
-
Integration with DevOps tools such as CloudBees CI and Jenkins®.
-
Interaction with cloud services.
-
Building and managing container images.
-
Scanning repositories for coding errors and security issues.
-
Integration with infrastructure automation tools like Helm.
| All CloudBees action repositories are listed at CloudBees, Inc. on GitHub. |
CloudBees actions are executed from .cloudbees/workflows in your source repository.
How to add an action to your workflow
You can directly add an action to your CloudBees Unify YAML file using the code editor. Refer to the example workflow or the links to action usage examples on the left pane for more information.
Alternatively, select from the UI action catalog to add an action to a step of your workflow.
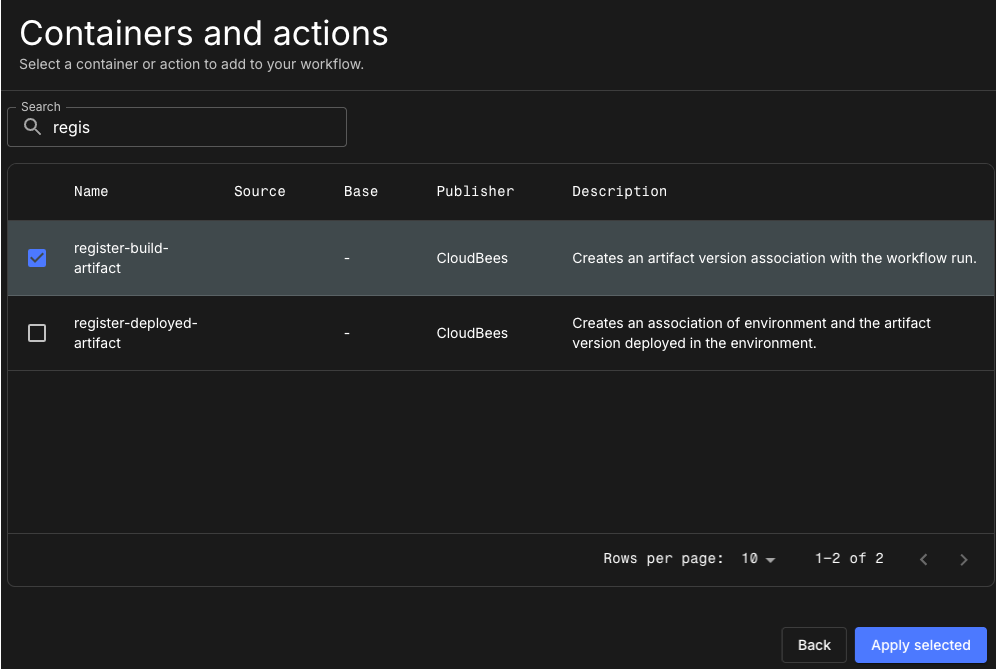
Specify the action inputs in the UI as in the example below:
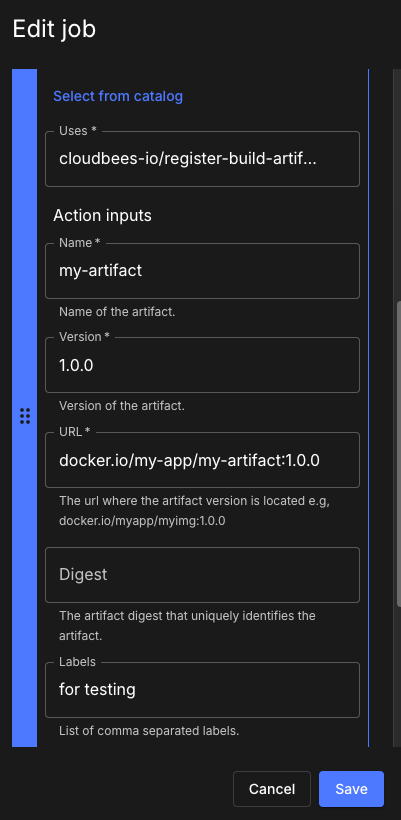
|
When using a CloudBees action URL in a workflow, short repository formats (for example, owner/repo) resolve exclusively to repositories hosted on GitHub SaaS. If you are using a source code management (SCM) provider other than GitHub, you must reference CloudBees actions using the full repository URL. For example, use |
Preconfigured actions
Simplify creating workflows by using preconfigured actions. An administrator can pre-populate an action to include specific input values, so the developer never needs to manage or input these. To learn more, refer to Preconfigured actions.
Security scan actions
CloudBees Unify enables you to run certain security scans either implicitly or explicitly.
Implicit security scanning
Implicit scans automatically trigger in response to specific events, ensuring continuous security checks without manual intervention.
| Event | Code that is scanned |
|---|---|
Creation of a new component. |
The linked repository source code. |
Commit code changes. |
The linked repository source code. |
A workflow runs successfully to build an artifact. |
The binary asset. |
Refer to implicit code security assessment to learn how to set up implicit scanning.
Explicit security scanning
Explicit scans are triggered manually, when you add a security action to your workflow. The following link to CloudBees actions for each type of security scan:
You can also perform explicit scans in GitHub Actions workflows integrated with CloudBees Unify. Refer to Using GitHub Actions with CloudBees Unify to learn more.
|
Ensure that your workflow and action code do not execute untrusted input. Use the following recommendations to harden your code against attackers:
|