The CloudBees OpenShift CLI plugin provisions the OpenShift CLI in your CloudBees CI jobs so that you can deploy applications or interact with an OpenShift environment.
Global configuration
OpenShift CLI installations can optionally be configured from page.
The default installer downloads the OpenShift CLI and installs it on the agent the first time it’s used by a job.
Alternatively, you can configure a custom installer to download a tar.gz archive from a custom location, or if an installation is not provided, oc will be used from the PATH.
Job configuration
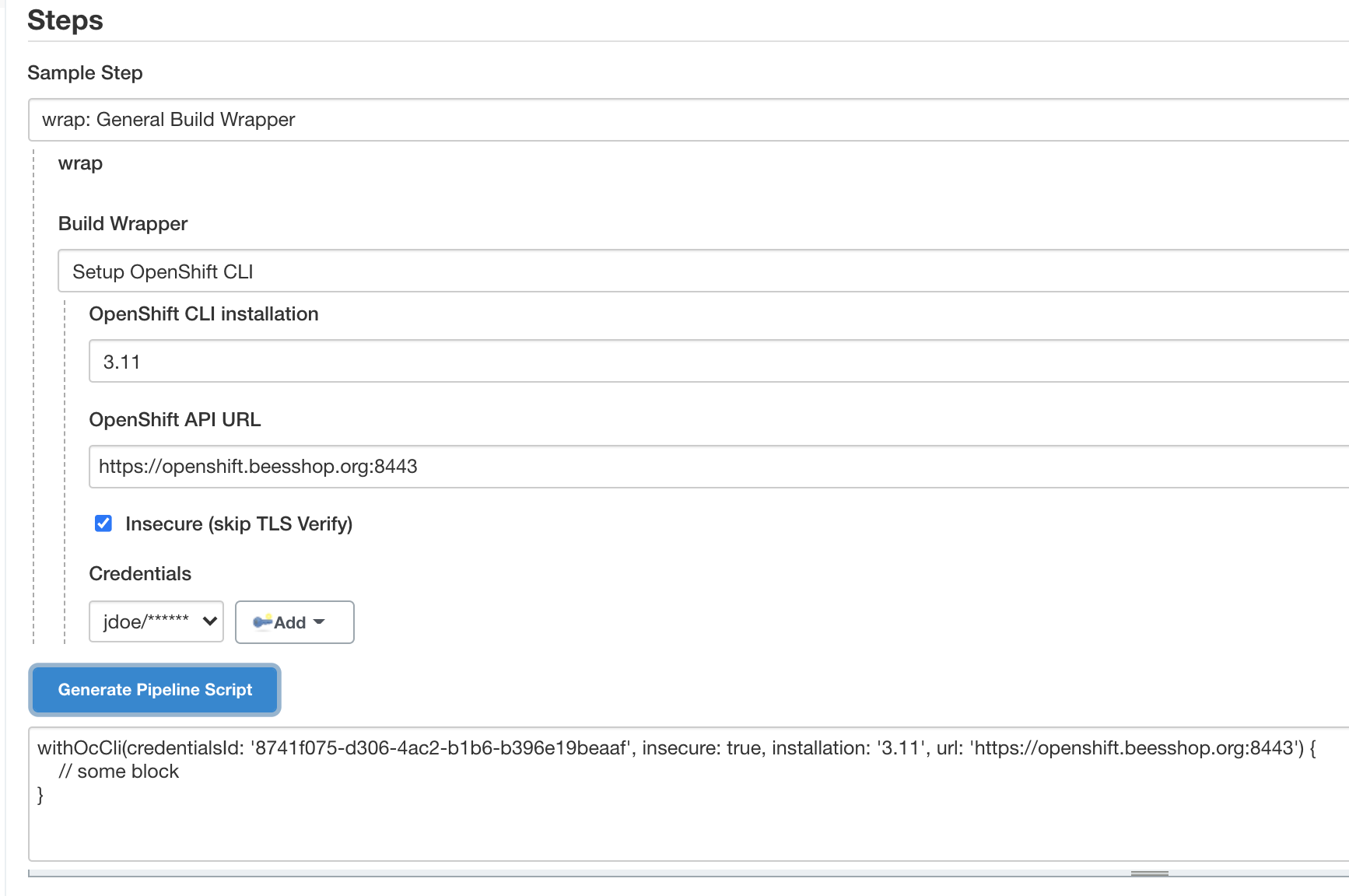
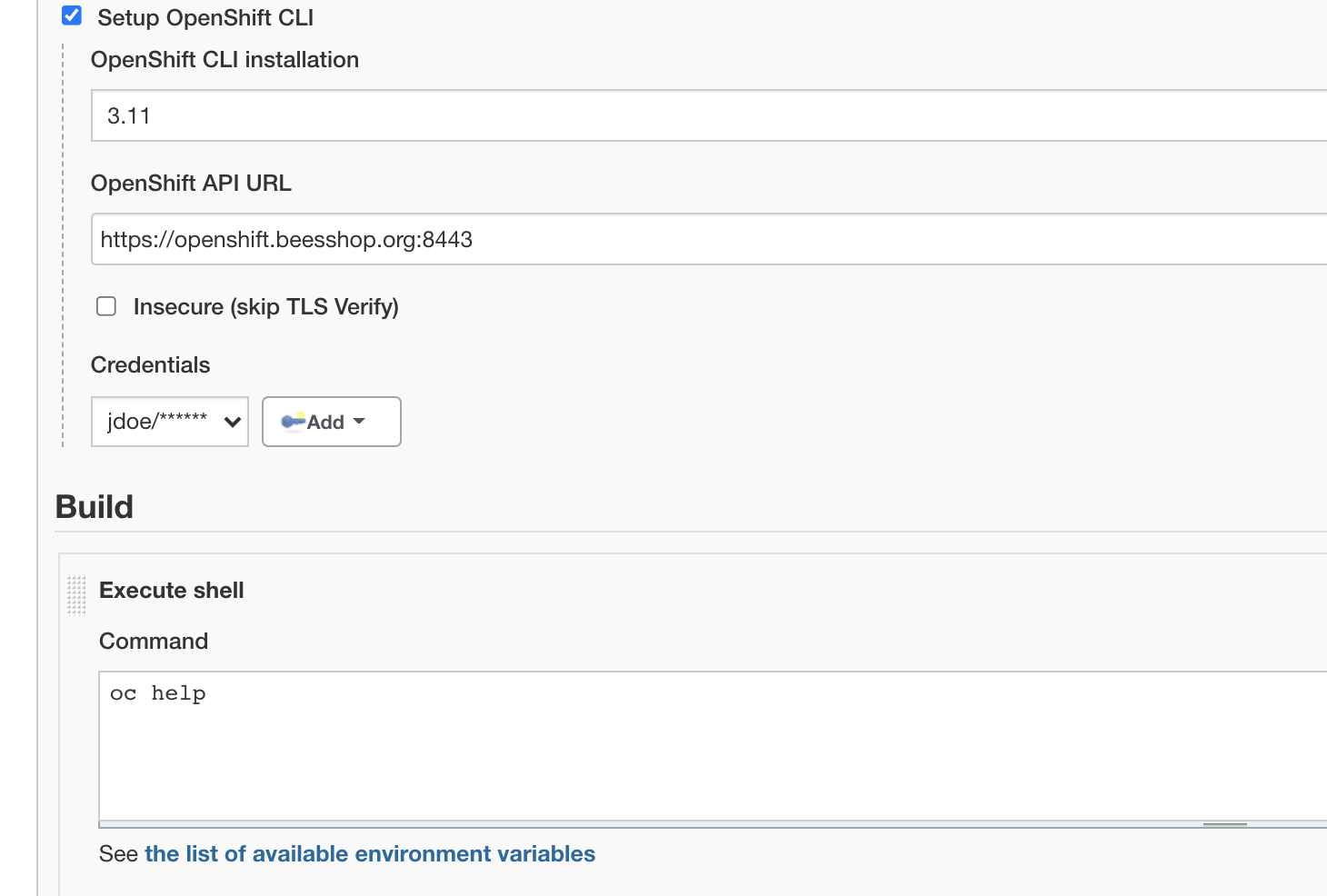
To enable the OpenShift CLI in a job, goto the Configuration page of the job and, in the Build Environment section, check Setup OpenShift CLI.
You can then select:
- CLI installation
-
OpenShift CLI installation to use. CLI can be configured for automatic installation on executor, please read next section.
- OpenShift controller URL
-
URL for the OpenShift controller endpoint URL.
- Insecure
-
Checking this option will disable the SSL certificate validation, so can be used to connect to an OpenShift controller which uses a self-signed HTTPS certificate. Please note this option introduce security risks and should not be used for production environments.
- Credentials
-
OpenShift credentials to set up so build steps within this job will run within an authenticated context.
Once the OpenShift CLI is set up in a job, you can use it in any Execute Shell or Execute Windows Batch Command step.
Use the OpenShift CLI in a Pipeline job
Once the OpenShift CLI is set up in the System Configuration, you can use it in any Pipeline job as a build wrapper.
OpenShift CLI Pipeline syntax
The Pipeline syntax looks like:
node { // ... withOcCli((1) installation: 'oc (latest)',(2) url: 'https://openshift.example.com:8443',(3) insecure: false,(4) credentialsId: 'openshift-credentials') {(5) sh 'oc scale --replicas=3 replicationcontrollers webapp'(6) } }
| 1 | "Setup OpenShift CLI" step name |
| 2 | Name of the OpenShift CLI version defined in the System Configuration screen (if undefined, oc will be used from PATH) |
| 3 | URL of the OpenShift controller endpoint (for example, https://openshift.example.com:8443) |
| 4 | Skip SSL validation when using a self-signed certificate for the API endpoint (this should always be false for production installations) |
| 5 | ID of the credentials to configure the OpenShift CLI (type OpenShift Username and Password) |
| 6 | oc commands used in sh steps, the OpenShift CLI is configured with the desired API endpoint and credentials. |
Evaluate oc commands result
Evaluating the result of the oc command is key to the logic of your Pipeline.
-
occommands return non-zero exit code in case of error and thus, shell steps will by default fail if anoccommand fails -
To capture the output of an
occommand in a Pipeline, usereturnStdout: trueas described in the Pipeline steps reference.