High Availability capabilities and architecture
CloudBees CI High Availability (HA) provides:
-
Controller Failover: If a controller fails, Pipeline builds normally run on that controller are automatically triggered or continued by another replica.
-
Horizontal scaling: One logical controller spreads its workload across multiple replicas evenly. Refer to Schedule builds and explicit load balancing for more information.
-
Rolling restart with zero downtime for CloudBees CI on modern cloud platforms: If a controller is restarted, replicas are replaced one by one, and the user experiences no downtime.
-
Rolling upgrades with zero downtime for CloudBees CI on modern cloud platforms: If a managed controller running in HA mode must be updated to a new version, replicas are incrementally updated without restarting the managed controller and with zero downtime.
CloudBees CI version
2.528.2.34846upgrades the Hazelcast library from version5.5to version5.6. This version transition makes rolling upgrades impossible. Refer to Upgrade managed controllers for more information. -
Auto-scaling for CloudBees CI on modern cloud platforms: You can set up managed controllers to increase the number of replicas, depending on the workload. They can upscale when the CPU usage overcomes a threshold and downscale when the conditions return to normal.
From a high-level perspective, these capabilities are provided using the architecture described in the image below:
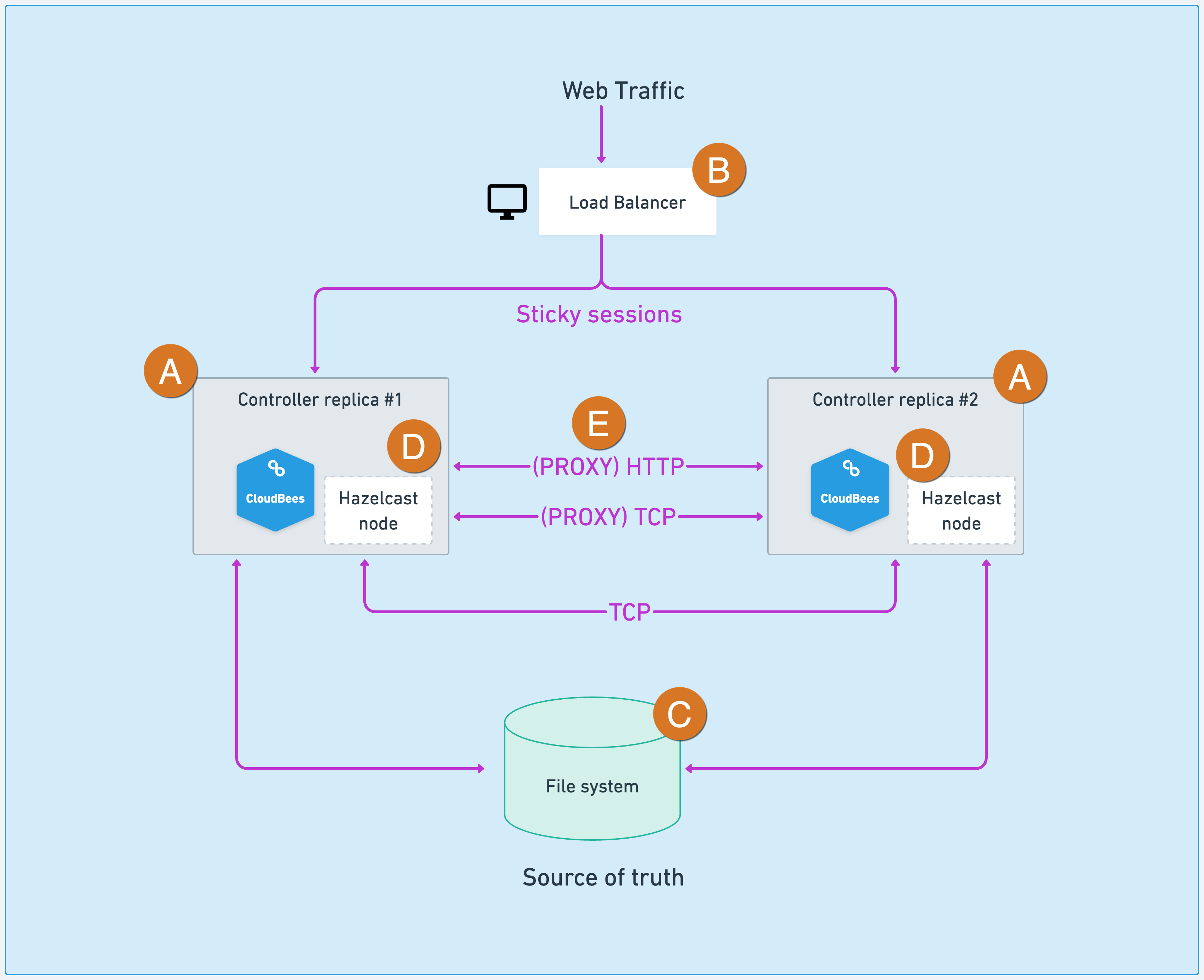
-
Controller replicas make HA possible.
-
The load balancer spreads the workload between the different controller replicas. Refer to Schedule builds and explicit load balancing for more information on how the load balancer distributes the workload and pipeline idioms, or steps, that are incompatible with HA.
-
A shared file system to persist controller content.
-
Controllers embed the Hazelcast distributed computation library, keeping their live state synchronized. No separate storage or setup is required.
-
If needed, CloudBees CI HA uses a reversed-proxy HTTP or TCP connection to access from one replica resources belonging or connected to other controller replicas. Resources like:
-
Running builds.
-
WebSocket inbound agents.
-
TCP Inbound agents from outside the CloudBees CI network.
As described above, as a requirement for HA, controller replicas must be able to connect using TCP connections for the Hazelcast nodes and by IP or hostname via HTTP.
-
High Availability (active/active) vs. High Availability (active/passive)
Unlike the older active-passive HA system, the mode discussed here is symmetrically active-active.
In the previous High Availability (active/passive), the cluster is not a symmetric cluster where controllers share workloads together. At any given point, only one of the replicas works as a controller. When a failover occurs, one of the replicas takes over the controller role. Users will experience a downtime comparable to rebooting a Jenkins controller in a non-HA setup.
With CloudBees CI High Availability (active/active) described in this guide, all controller replicas are always working, and the controller’s workload is spread between them. When one of the replicas fails, other replicas adopt all of its builds, and the user does not have any downtime.